I. Definition, Historical Perspective & Epidemiology
Zollinger–Ellison Syndrome (ZES) is a rare disorder characterized by gastrin-secreting tumors (“gastrinomas”) of the pancreas or duodenum. These tumors lead to excessive gastric acid secretion, resulting in recurrent, treatment-resistant peptic ulcers, severe gastroesophageal reflux, and diarrhea.
- ZES accounts for <1% of peptic ulcer disease cases.
- May occur sporadically or as part of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1 (MEN1).
- Peak incidence: 30–60 years; men and women equally affected.
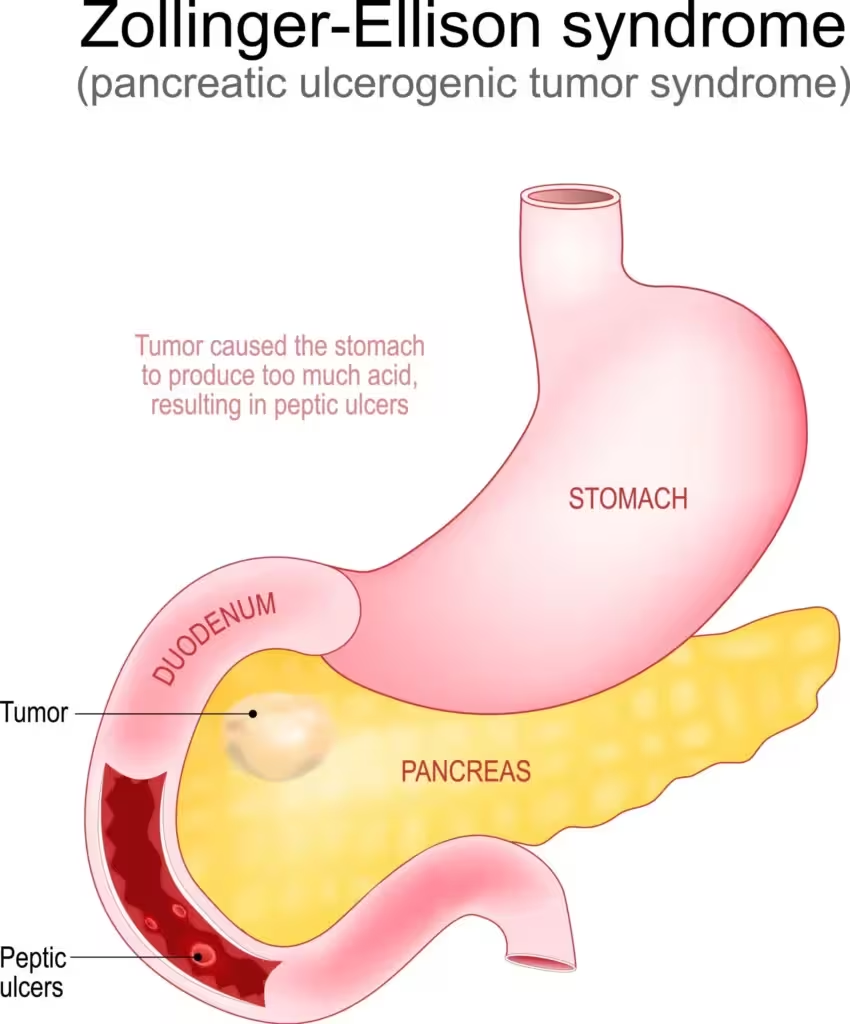
II. Pathophysiology
1. Gastrinoma Biology
- Gastrinomas are neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), most commonly in the “gastrinoma triangle” (pancreatic head, duodenum, and peripancreatic soft tissue), and less often in lymph nodes or elsewhere.
- Malignancy: Up to 60% are malignant, capable of regional and hepatic metastasis.
2. Mechanism—Gastrin Overproduction
- Unregulated gastrin secretion (often >10x normal baseline) causes gastric parietal cell hyperplasia and massive gastric acid hypersecretion.
- Gastric pH is often <2, even after fasting.
3. Resultant Clinical Effects
- Recurrent, multiple, and atypical peptic ulcers: Especially duodenal ulcers distal to the bulb, or ulcers refractory to standard anti-ulcer therapy.
- Diarrhea, steatorrhea: Acid inactivates pancreatic enzymes (impairing fat digestion) and damages mucosa, leading to nutrient malabsorption.
- Chronic acid exposure → esophagitis, stricture, Barrett’s esophagus.
III. Clinical Features
- Severe, recurrent peptic ulcer disease (often multiple, post-bulbar)
- Gastroesophageal reflux symptoms
- Diarrhea and steatorrhea (in up to 50–75% cases; may be the only presenting sign)
- Weight loss and malnutrition with advanced disease
- MEN1 features (pituitary, parathyroid, pancreatic tumors) in about 25% of cases
IV. Diagnosis
1. Clinical Suspicion
- Ulcers refractory to standard treatment
- Multiple or atypically located ulcers (distal duodenum, jejunum)
- Unexplained recurrent ulcers with diarrhea
2. Key Diagnostic Tests
- Fasting serum gastrin level (>10x upper limit of normal, often >1000 pg/mL): Most reliable initial test.
- Caution: Discontinue proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) for 1–2 weeks prior if possible (can elevate gastrin).
- Gastric pH measurement (<2): Demonstrates intact or increased acid secretion, supports diagnosis.
- Secretin stimulation test: Secretin paradoxically increases gastrin in ZES but not in other causes of hypergastrinemia.
- Imaging: Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy (Octreoscan), endoscopic ultrasound, CT/MRI to localize gastrinoma.
- MEN1 evaluation: Check serum calcium, parathyroid hormone, and pituitary hormones.
V. Differential Diagnosis
- Peptic ulcer disease due to H. pylori, NSAIDs
- Gastric outlet obstruction
- Hypercalcemia/hyperparathyroidism
- Other causes of hypergastrinemia: chronic atrophic gastritis, retained antrum, vagotomy ()
VI. Management
A. Acid Suppression—Mainstay of Therapy
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs):
- Omeprazole, pantoprazole, esomeprazole, lansoprazole
- PPIs are the drug of choice, suppressing acid secretion by irreversibly blocking the H⁺/K⁺-ATPase in parietal cells.
- Dosing: Often requires much higher than conventional doses (e.g., omeprazole 60–120mg/day in divided doses) to maintain gastric pH >3.
- H2-receptor antagonists: Less effective; may require massive and inconvenient dosing.
B. Surgical and Curative Therapy
- Surgical resection of localized tumor (if feasible and no metastases).
- MEN1 patients: Surgery usually reserved for aggressive or symptomatic tumors, as multiple/microscopic tumors are the norm.
- Liver-directed therapy: Resection, radiofrequency ablation, embolization for metastatic disease.
- Somatostatin analogs (octreotide, lanreotide): Used for symptomatic or metastatic gastrinomas when surgery is not feasible.
- Chemotherapy or targeted therapy: For progressive, metastatic disease; e.g., streptozocin, 5-FU, everolimus.
C. Management of Diarrhea and Nutritional Support
- Correct fluid/electrolyte imbalance
- Pancreatic supplements if steatorrhea
- Parenteral nutrition if severe malabsorption.
VII. Prognosis
- Survival: Dramatically improved with effective gastric acid suppression (PPIs).
- Prognostic factors: Presence of liver metastases (major determinant), MEN1 association, tumor grade.
- Lifelong surveillance is necessary, as recurrence/metastasis can occur after long remission periods.
VIII. Pharmacological Notes (For Examinations)
- PPIs are first-line due to powerful, irreversible inhibition of gastric acid secretion.
- Octreotide: Long-acting somatostatin analog, inhibits gastrin release.
- Avoid abrupt withdrawal of acid suppression: Risk of severe ulcer flare or GI bleeding.
- Cholecystokinin-B/gastrin receptor antagonists: Experimental, not standard therapy.
IX. Key Learning Points
- Zollinger–Ellison Syndrome is a gastrin-secreting tumor syndrome—think of it with refractory, multiple, or post-bulbar ulcers, especially with diarrhea.
- Serum gastrin >1000 pg/mL with low gastric pH is virtually diagnostic.
- Management is primarily with high-dose PPIs; surgery for localized disease, and somatostatin analogs for unresectable or metastatic settings.
- MEN1 association is crucial—always screen for other endocrine neoplasms.
X. Table: Comparison—Peptic Ulcer Disease vs. ZES
| Feature | Common Peptic Ulcer | ZES |
|---|---|---|
| Ulcer location | Duodenal bulb, stomach | Multiple, distal duodenum/jejunum |
| Gastrin level | Normal/slightly ↑ | Markedly ↑ (>10x normal) |
| Acid secretion | Normal/high | Very high, basal output>15 mEq/h |
| Response to therapy | Good (PPI/H2RA) | Poor without very high PPI |
| Associated symptoms | Dyspepsia, pain | Pain, diarrhea, steatorrhea |
| Association with MEN1 | Absent | Present in ~25% |
XI. References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 13th ed. (2018). Chapter: Gastrointestinal Pharmacology; Hypersecretory States.
- Katzung BG, Trevor AJ. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. 15th ed. (2023). Chapter: Drugs Used in Acid-Peptic Disorders.
- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 20th ed. (2022). Chapter: Peptic Ulcer Disease and Related Disorders.
- Ritter JM, Flower R, Henderson G, et al. Rang & Dale’s Pharmacology. 10th ed. (2023). “Drugs for gastrointestinal disorders.”
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.

