Introduction
“Alcohol” in pharmacology typically refers to ethanol, the psychoactive ingredient of alcoholic beverages, but also includes toxic congeners—methanol, ethylene glycol, isopropanol. All share the –OH functional group yet differ in metabolism and clinical impact. This review contrasts their pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, toxicology and therapeutic considerations.
Ethanol
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: rapid passive diffusion; 80 % from small intestine, 20 % gastric. Peak blood conc. 30–90 min (faster on empty stomach).
- Distribution: total body water; Vd ≈ 0.6 L/kg (men) vs. 0.5 L/kg (women).
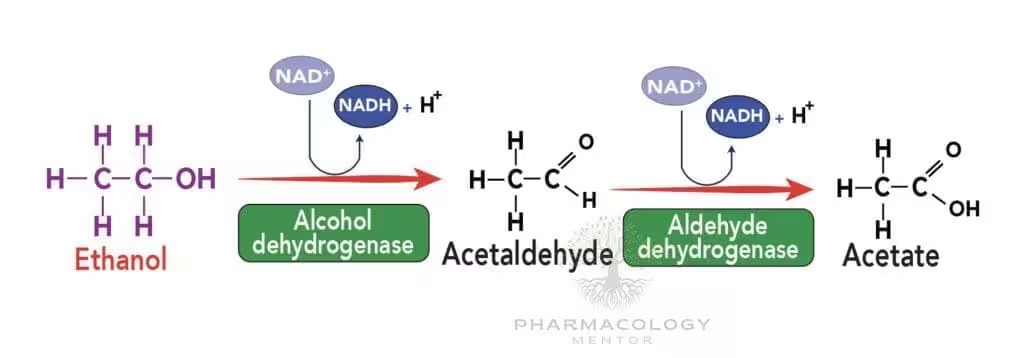
- Metabolism: hepatic oxidation ≈ 90 %. Two-step pathway (see Table 1):
ADH → acetaldehyde, then ALDH → acetate. Microsomal ethanol-oxidising system (MEOS, CYP2E1) induced with chronic intake, ↑ clearance & drug interactions. - Elimination: zero-order (constant rate) at 7–10 g/h in average adult; <1 % excreted unchanged in breath, urine, sweat.
| Step | Enzyme / Cofactor | Product | Inhibitors / Variants |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH1B*2 ↑ Vmax) NAD+ → NADH | Acetaldehyde | Fomepizole, pyrazoles |
| 2 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 (mitochondrial) | Acetate → CO2 + H2O | Disulfiram, ALDH2*2 polymorphism |
Acute Pharmacodynamics
- CNS: dose-dependent depression via GABAA potentiation, NMDA inhibition, ↑ endogenous opioids.
- CV: vasodilation (cutaneous flushing), slight ↑ HR; high doses depress myocardium.
- Endocrine/metabolic: hypoglycaemia (inhibits gluconeogenesis), diuresis (↓ ADH release), ↑ lactate (NADH excess).
- Behavioural staging: euphoria (BAC 0.02–0.05 %), incoordination (0.08 %), coma >0.3 %, respiratory depression >0.45 %.
Chronic Effects
- Hepatic: fatty liver → alcoholic hepatitis → cirrhosis.
- GI: gastritis, pancreatitis, malabsorption, cancer risk (oropharynx, oesophagus).
- Neurological: peripheral neuropathy, Wernicke–Korsakoff (thiamine deficit), cerebellar degeneration.
- Cardiovascular: dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertension; modest intake may raise HDL.
- Foetal alcohol spectrum disorders from in-utero exposure.
Tolerance & Dependence
Chronic intake induces pharmacokinetic tolerance (CYP2E1 up-regulation) and functional tolerance (receptor down-regulation). Abrupt cessation → sympathetic overdrive, tremor, hallucinosis, seizures, delirium tremens (treated with benzodiazepines ± thiamine).
Therapeutic & Preventive Agents
| Drug | Mechanism | Clinical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Disulfiram | Irreversible ALDH inhibition → ↑ acetaldehyde → aversive reaction | Deterrent (supervised) |
| Naltrexone (oral / depot) | μ-opioid antagonist ↓ reward craving | First-line relapse prevention |
| Acamprosate | Modulates glutamatergic tone (NMDA) → restores balance | Maintains abstinence |
| Diazepam, chlordiazepoxide | GABAA potentiation | Withdrawal management |
Other Toxic Alcohols
Methanol
- Sources: windshield-washer fluid, industrial solvents, illicit spirits.
- Toxic metabolite: formic acid → metabolic acidosis, optic nerve injury (“snowfield” vision), basal ganglia necrosis.
- Treatment: fomepizole (ADH inhibitor) or IV ethanol, bicarbonate, folinic acid, haemodialysis if pH<7.25, methanol >20 mg/dL or visual symptoms.
Ethylene Glycol
- Sources: antifreeze, brake fluid.
- Metabolism: glycolic → glyoxylic → oxalic acid; precipitates Ca-oxalate crystals → renal failure.
- Clinical phases: neurologic (0–12 h), cardiopulmonary (12–24 h), renal (24–72 h).
- Treatment: fomepizole/ethanol, dialysis, thiamine & pyridoxine co-factors to shunt metabolism.
Isopropanol
- Sources: rubbing alcohol, hand sanitisers.
- Metabolite: acetone (non-acidic) → profound CNS depression, ketosis without acidosis.
- Management: supportive (airway, fluids); ADH blockade not required.
Key Drug Interactions with Ethanol
- Acute ethanol: inhibits hepatic CYPs → ↑ warfarin, phenytoin levels.
- Chronic ethanol: induces CYP2E1 → ↑ hepatotoxicity of paracetamol, ↑ clearance of some drugs.
- Synergistic CNS depression with benzodiazepines, opioids, H1 antihistamines.
- Hypoglycaemic potentiation with insulin or sulfonylureas.
Clinical Pearls
- Ethanol exhibits zero-order elimination at typical blood levels; small dose increases markedly prolong impairment.
- Formic and oxalic acids, not methanol or ethylene glycol themselves, cause end-organ toxicity → block ADH early.
- Osmolar gap & anion gap together guide diagnosis of toxic alcohol ingestions.
- Thiamine 100 mg IV before glucose prevents Wernicke encephalopathy in alcohol-dependent patients.
- Combination pharmacotherapy (e.g., naltrexone + acamprosate) may improve long-term abstinence rates.
References
- Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollmann BC, editors. Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 14th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2022.
- Trevor AJ, Katzung BG, Kruidering-Hall M. Pharmacology: Examination & Board Review. 13th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2021.
- Rang HP, Dale MM, Ritter JM, Flower RJ, Henderson G. Rang & Dale’s Pharmacology. 9th ed. London: Elsevier; 2020.
- Kraut JA, Mullins ME. Toxic alcohols. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(3):270-80.
- Lal R, Pattanayak R. Alcohol use disorders. Indian J Med Res. 2017;146(6):593-602.
- Wilde M, Bibi A, Saran JS. Management of alcohol withdrawal and intoxication. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.

