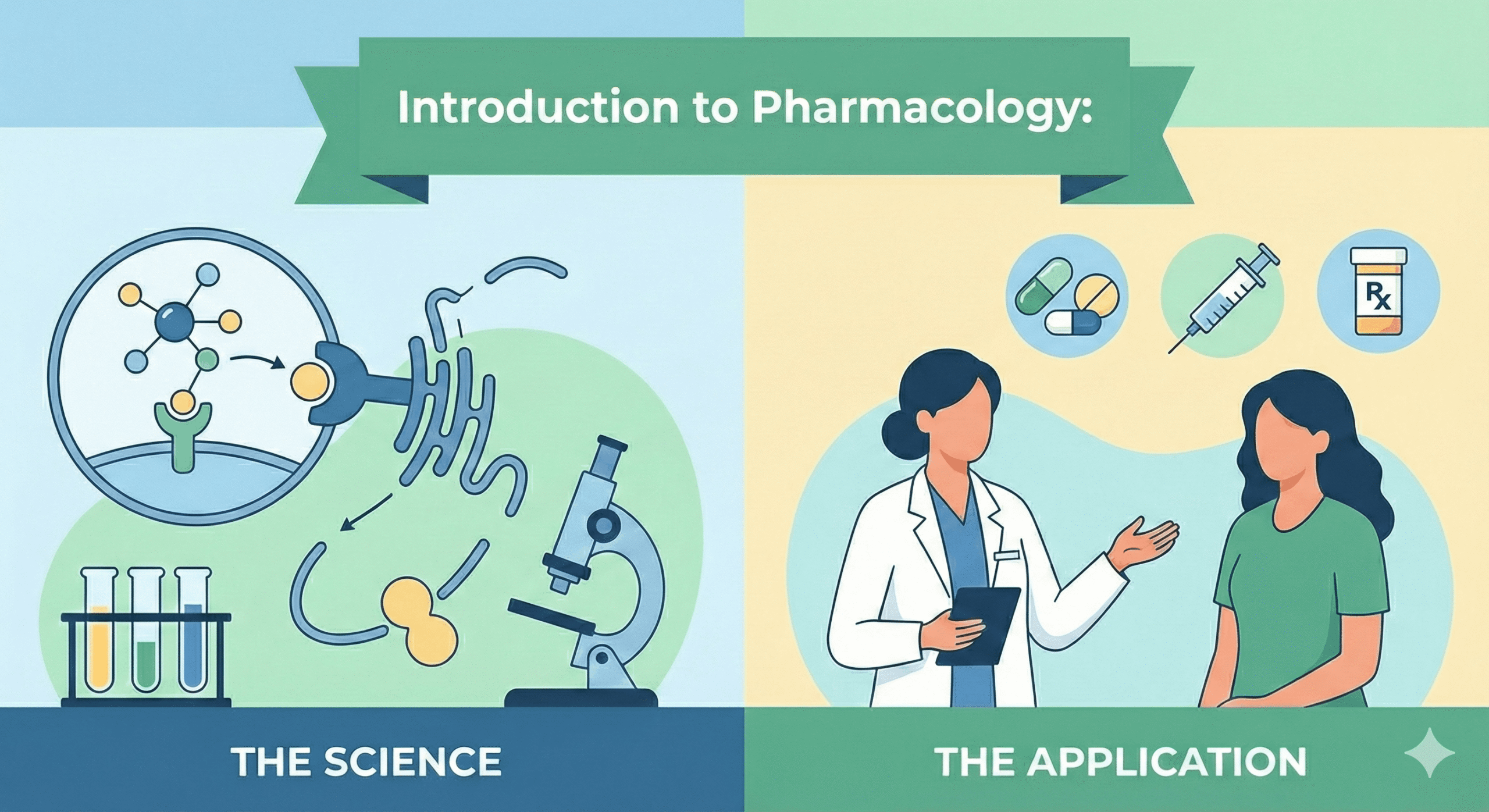
1 · Definition & Conceptual Overview
Pharmacology is the scientific discipline that investigates how chemical agents (drugs) interact with living systems to modify physiological or biochemical functions. At its core, pharmacology seeks to explain:
- The mechanisms of action of drugs at molecular, cellular, organ and whole-body levels.
- The quantitative relationship between dose (or concentration) and biological effect (pharmacodynamics).
- The absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) of drugs (pharmacokinetics).
By integrating these perspectives, pharmacology underpins rational therapeutics — i.e., the safe and effective use of medicines in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of disease.
2 · Historical Evolution
Humanity’s engagement with bioactive substances dates back to antiquity, but pharmacology emerged as an experimental science only in the nineteenth century when advances in chemistry, physiology and microscopy converged. Landmark milestones include:
- 1805 — Sertürner isolates morphine from opium, heralding the era of pure alkaloids.
- 1874 — Oswald Schmiedeberg founds the first institute of pharmacology in Strasbourg, emphasising controlled experimentation on isolated organs.
- 1905–1940 — discovery of adrenaline, acetylcholine and histamine as endogenous mediators, laying the groundwork for receptor theory.
- 1940–1960 — antibiotics, corticosteroids and the random-screening model transform therapeutics.
- 1970–present — molecular cloning of receptors, recombinant biologics and structure-based drug design recalibrate the field toward precision medicine.
3 · Scope of Modern Pharmacology
Contemporary pharmacology spans a continuum from basic bench research to bedside application:
- Receptor biophysics & signal transduction
- Pharmacokinetic modelling (compartmental, physiologically based)
- Toxicology — study of adverse effects and poisoning
- Clinical pharmacology — optimisation of drug therapy in humans
- Pharmacoepidemiology & pharmacovigilance — population-scale safety monitoring
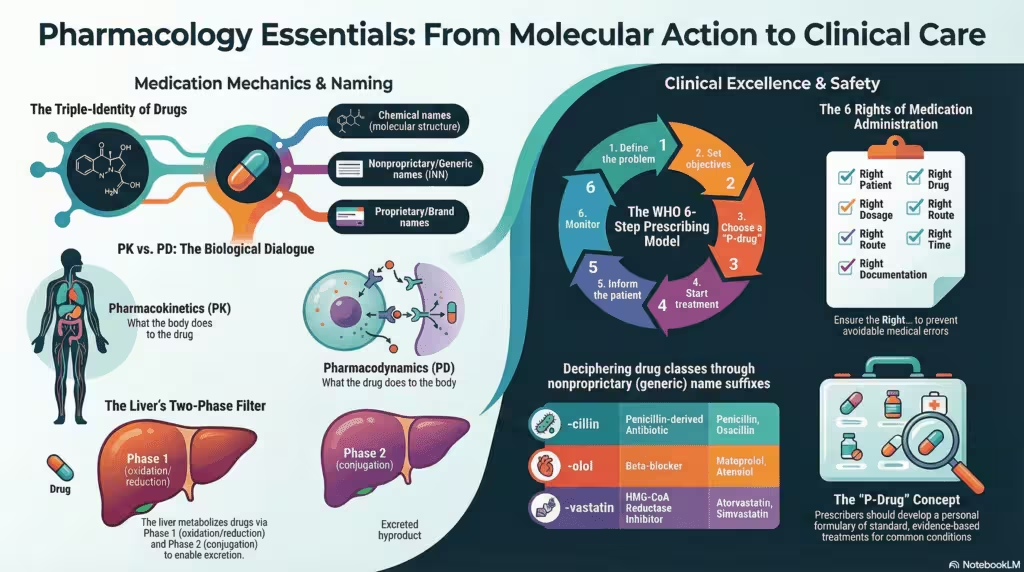
4 · Foundational Terminology
- Drug — any chemical entity that can modify biological systems when administered in adequate amounts.
- Pharmacodynamics (PD) — what the drug does to the body.
- Pharmacokinetics (PK) — what the body does to the drug.
- Agonist — molecule that binds to a receptor and elicits a functional response.
- Antagonist — molecule that binds without activating, blocking agonist action.
- Efficacy — maximum response achievable with a drug.
- Potency — amount (dose or concentration) of drug needed to produce a given effect.
5 · Major Sub-disciplines
5.1 Systems & Organ Pharmacology
Explores drug actions on specific organ systems (e.g., cardiovascular, respiratory, nervous). Integration with pathophysiology guides therapeutic choice.
5.2 Molecular Pharmacology
Investigates drug-target interactions at atomic resolution via crystallography, cryo-EM and computer simulations. Critical for rational compound optimisation.
5.3 Clinical Pharmacology
Translates laboratory discoveries into human application, encompassing phase I–IV trials, drug–drug interactions, therapeutic drug monitoring and evidence-based prescribing.
5.4 Toxicology
Focuses on harmful effects: acute poisoning, chronic organ toxicity, teratogenicity and carcinogenesis. Risk–benefit evaluation is inseparable from therapeutic decision-making.
6 · The Drug-Development Pipeline
- Target Identification — validate a biological pathway implicated in disease.
- Lead Discovery — screening libraries (small molecules, peptides, antibodies).
- Lead Optimisation — improve potency, selectivity, ADME properties.
- Pre-clinical Testing — in vitro assays and animal studies for efficacy and safety.
- Clinical Phases I–III — human trials to establish safety, dosage and efficacy.
- Regulatory Review — dossier submission to agencies (FDA, EMA).
- Post-marketing (Phase IV) — pharmacovigilance and rare-event detection.
7 · Dose–Response Relationships
Graded curves depict response magnitude against concentration, typically sigmoidal when plotted on a semi-log axis, yielding:
- EC50 — concentration giving 50 % maximal effect.
- Emax — plateau indicating full efficacy.
Quantall curves (all-or-nothing responses) enable computation of ED50, TD50 and LD50 for population studies.
8 · Fundamentals of Receptor Theory
Receptors are macromolecular sites that bind ligands with high specificity, translating occupancy into biological effect. Key models:
- Occupancy Theory — response proportional to fraction of occupied receptors (Clark, 1933).
- Two-State Model — receptors exist in active (R*) and inactive (R) conformations; ligands shift equilibrium.
- Signal Amplification — G-protein cascades and kinase networks allow small ligand binding events to produce large cellular outputs.
9 · Pharmacokinetics versus Pharmacodynamics
| Dimension | Pharmacokinetics | Pharmacodynamics |
|---|---|---|
| Core Question | “How does plasma concentration change over time?” | “What biological effect accompanies a given concentration?” |
| Primary Variables | ADME: absorption rate, bioavailability (F), volume of distribution (Vd), clearance (Cl), half-life (t½) | Receptor affinity, intrinsic efficacy, downstream signalling |
| Clinical Tools | Therapeutic drug monitoring, dose adjustments. | Biomarker evaluation, pharmacodynamic endpoints. |
10 · Therapeutic Index & Drug Safety
The therapeutic index (TI) = LD50 ⁄ ED50. A wide TI denotes relative safety (e.g., penicillin); a narrow TI (e.g., digoxin, warfarin) mandates plasma monitoring. Pharmacovigilance systems capture post-marketing adverse drug reactions (ADRs) to refine safety profiles continuously.
11 · Evidence-Based Prescribing
- Randomised controlled trials remain the gold standard for efficacy.
- Systematic reviews and meta-analyses synthesise data across studies.
- Clinical pharmacogenomics tailors therapy based on genetic variants (e.g., CYP2C19, HLA-B*57:01).
- Stewardship programmes promote rational antibiotic use to limit resistance.
12 · Emerging Frontiers
- Biologic therapies — monoclonal antibodies, CAR-T cells, RNA therapeutics.
- Artificial intelligence in in silico drug discovery and adaptive trial design.
- Nanopharmacology — targeted delivery vehicles (liposomes, dendrimers).
- Real-world data & digital phenotyping reshape post-marketing surveillance.
13 · Key Learning Points
- Pharmacology integrates mechanistic insight (PD) with time-concentration profiles (PK) to enable rational therapy.
- Receptor theory provides the conceptual framework for drug–target interactions and signal transduction.
- Dose–response analysis distinguishes potency from efficacy and informs dosage selection.
- The drug-development pathway spans discovery to post-marketing; each phase interrogates safety and efficacy at increasing scale.
- Evidence-based prescribing, pharmacogenomics and pharmacovigilance collectively safeguard patient outcomes.
14 · Conclusion
Pharmacology stands at the crossroads of chemistry, biology and medicine, translating molecular events into therapeutic realities. By elucidating how drugs interact with living organisms and how organisms respond in turn, pharmacology empowers clinicians and researchers to innovate safer, more effective treatments for the ever-evolving landscape of human disease.
References
- Rang HP, Dale MM, Ritter JM, Flower RJ, Henderson G. Rang & Dale’s Pharmacology. 9th ed. London: Elsevier; 2020.
- Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollmann BC, editors. Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 14th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2022.
- Neal MJ. Medical Pharmacology at a Glance. 9th ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell; 2019.
- Trevor AJ, Katzung BG, Kruidering-Hall M. Pharmacology: Examination & Board Review. 13th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2021.
- Benet LZ, Kroetz DL, Sheiner LB. Pharmacokinetics: the dynamics of drug absorption, distribution, and elimination. In: Brunton LL, editor. Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 14th ed. McGraw-Hill; 2022. p. 53-134.
- Nies AS, Spielberg SP. Principles of therapeutics. In: Brunton LL, editor. Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 14th ed. McGraw-Hill; 2022. p. 37-52.
Molecule_to_Bedside_Pharmacology-rev
Also visit for more information:
https://pharmalearn.ijcbr.com/blog/introduction-to-pharmacology
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.