Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is the process by which microorganisms evolve to withstand the effects of drugs that were once effective against them. Understanding the mechanisms of resistance is vital for clinicians, microbiologists, and policy makers in managing infections and designing stewardship interventions.
What Is Antimicrobial Resistance?
AMR occurs when previously susceptible microbes (bacteria, fungi, viruses, or parasites) acquire the ability to survive exposure to antimicrobial agents. The microbes may become less sensitive or completely resistant, rendering standard treatments less effective or ineffective.
Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance
Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance:
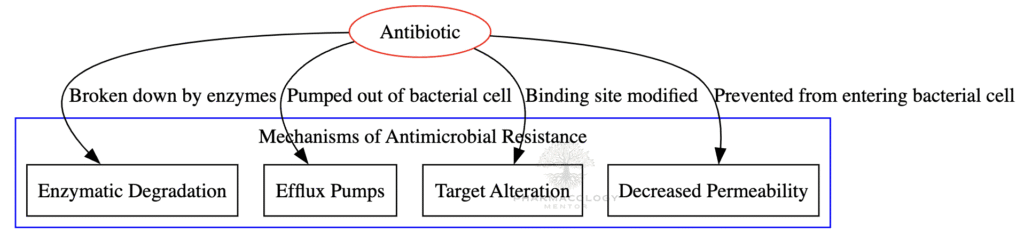
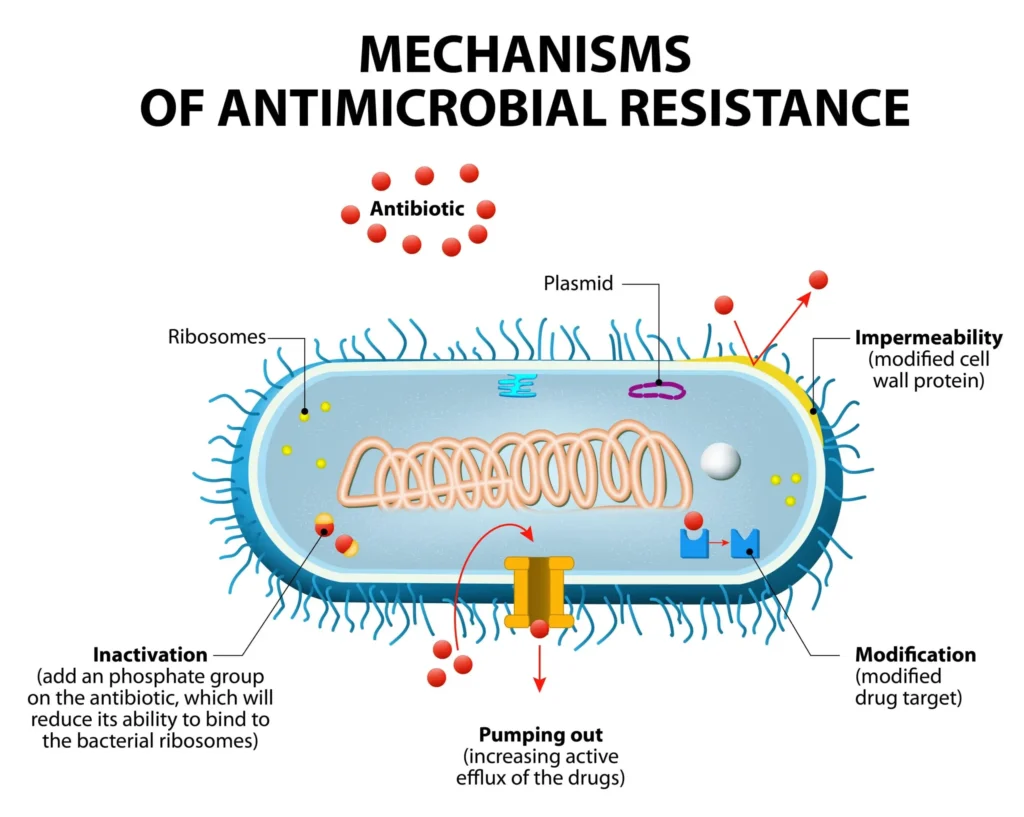
| Mechanism | Description & Examples |
|---|---|
| Drug inactivation/modification | Enzymatic breakdown or alteration of the drug by microbial enzymes. |
| – β-lactamases (penicillinases, cephalosporinases) hydrolyze β-lactams. | |
| – Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes (acetylation, phosphorylation). | |
| Alteration of drug target | Mutation or enzymatic modification of the antibiotic’s binding site. |
| – PBP2a (altered penicillin-binding protein) in MRSA. | |
| – Mutant DNA gyrase/topoisomerase IV genes in quinolone resistance. | |
| – Methylation of 23S rRNA (erm genes) conferring macrolide/lincosamide resistance. | |
| Reduced permeability | Modifications in outer membrane proteins (porins) reduce drug entry. |
| – Carbapenem resistance in Gram-negatives due to porin loss. | |
| Active efflux pumps | Drug-specific or multidrug pumps expel antibiotics before action. |
| – Tetracycline, macrolide/Pseudomonas efflux pumps. | |
| Bypass of metabolic pathways | Pathogen acquires alternative enzymatic pathway or target. |
| – Sulfonamide resistance by alternative dihydropteroate synthase. | |
| Biofilm formation | Dense microbial communities shield cells from antibiotics/immune system. |
| – Chronic Pseudomonas infection in cystic fibrosis. |
Genetic Basis of Resistance
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Mutation | Spontaneous changes in chromosomal DNA may alter drug target or regulatory pathways. Rapid selection under antibiotic pressure. |
| Horizontal Gene Transfer | Movement of resistance genes via plasmids (conjugation), phages (transduction), or naked DNA (transformation) between bacteria. Enables rapid spread of resistance within and between species. |
Types of Resistance
- Intrinsic resistance: Innate, natural insensitivity (e.g., Gram-negatives to vancomycin, Pseudomonas to many drugs).
- Acquired resistance: Gained via mutation or gene transfer (e.g., ESBLs, MRSA, VRE).
Clinical Impact
- Failure of standard therapy.
- Prolonged illness, increased complications, mortality, healthcare costs.
- Necessitates use of broader-spectrum, more toxic, less effective, or more expensive alternatives.
Notable Resistant Pathogens (“ESKAPE” pathogens & others)
| Pathogen | Major Resistance Mechanism(s) | Key Clinical Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| Enterococcus faecium (VRE) | VanA/B genes alter D-Ala-D-Lac | Nosocomial infections |
| Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA/VRSA) | mecA → PBP2a (MRSA); vanA (VRSA) | Skin, pneumonia, sepsis, endocarditis |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | ESBLs, carbapenemases (KPC, NDM) | UTI, pneumonia, sepsis |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | OXA/NDM-type carbapenemases, efflux | Wound, pneumonia, critical care |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Porin loss, efflux, metallo-β-lactamases | Pneumonia, burn, ICU infections |
| Enterobacter cloacae | AmpC β-lactamase, porin loss, efflux | UTI, pneumonia, sepsis |
Combating Antimicrobial Resistance
- Stewardship: Optimize therapy, minimize unnecessary use.
- Surveillance: Monitor resistance trends locally/nationally.
- Infection control: Hand hygiene, isolation, environmental cleaning.
- Rapid diagnostics: Enable early detection and targeted therapy.
- Research: Develop new antibiotics, alternative therapies, and vaccines.
References
- Habboush Y, Guzman N. Antibiotic Resistance. In: StatPearls [Internet]. 2023 Jun 19.
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 14th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2022.
- WHO. Implementing the global action plan on antimicrobial resistance. WOAH, 2024.
- Belay WY, et al. Mechanism of antibacterial resistance, strategies and next-generation approaches. Front Pharmacol. 2024.
- CDC. About Antimicrobial Resistance. Jan 2025.
Antimicrobial resistance
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.

