Malaria is a major infectious disease caused by Plasmodium parasites, transmitted to humans by female Anopheles mosquitoes. Despite global control efforts, malaria remains a significant cause of morbidity and mortality, especially in resource-limited settings.
I. Epidemiology & Public Health Burden
- Global Estimate: ~241 million cases, >600,000 deaths annually (WHO 2021).
- High-Risk Regions: Sub-Saharan Africa (>90% cases), Southeast Asia, Latin America.
- At-Risk Groups: Young children, pregnant women (placental malaria), travelers, immunocompromised.
- Recent developments: Increased focus on elimination, mass drug administration in endemic foci, RTS,S/AS01 malaria vaccine in pilot introduction.
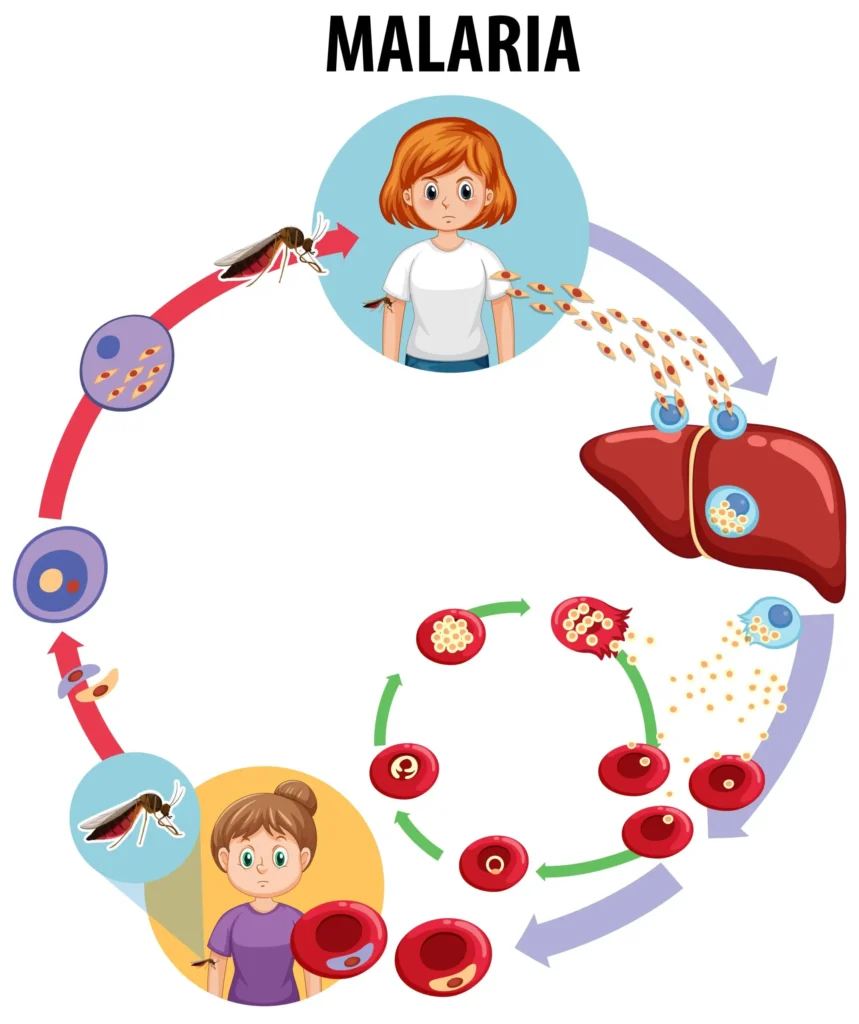
II. Plasmodium Species and Life Cycle
| Species | Prevalence | Features |
|---|---|---|
| P. falciparum | Most common, most severe | Cerebral malaria, severe anemia |
| P. vivax | Second most common | Relapses (hypnozoites), broad distribution |
| P. ovale | Africa, rare elsewhere | Relapses (hypnozoites) |
| P. malariae | Worldwide, low incidence | Chronic/inapparent infection |
| P. knowlesi | SE Asia | Severe, zoonotic |
Life Cycle Highlights:
- Sporozoite transmission: Injected via mosquito bite, travel to liver.
- Exoerythrocytic (liver) phase: Cells mature into schizonts, release merozoites.
- Erythrocytic phase: Merozoites invade red blood cells; repeated cycles of lysis cause symptomatic malaria.
- Gametocyte formation: Sexual stages taken up by another mosquito, perpetuating the cycle.
- Hypnozoites: Dormant liver forms (P. vivax, P. ovale) cause late relapses.
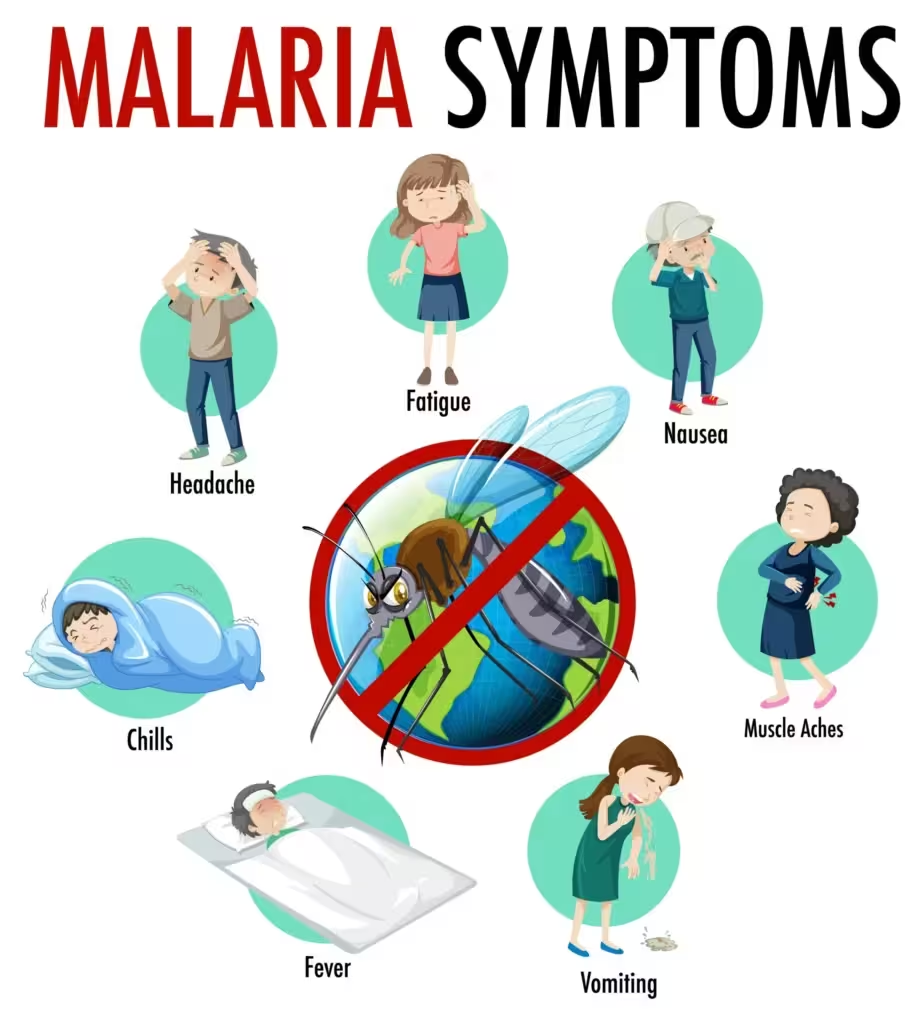
III. Clinical Presentation
- Uncomplicated malaria: Periodic fever (classic tertian/quartan cycle), chills, sweats, headache, malaise, myalgia.
- Severe malaria: Confusion, seizures (cerebral), shock and organ dysfunction (renal, hepatic), acidosis, respiratory distress, severe anemia, hypoglycemia (especially children/pregnant women).
- Signs: Splenomegaly, jaundice, dark urine (hemoglobinuria, “blackwater fever”).
IV. Diagnosis
- Microscopy
- Thick and thin blood smears: Gold standard, enables species identification, quantification of parasitemia.
- RDTs (Rapid Diagnostic Tests)
- Detect antigens (HRP2 for P. falciparum, LDH for pan-malarial warning).
- Useful in poor-resource/field settings.
- PCR & Molecular Diagnostics
- High sensitivity/specificity, mostly for research or complex diagnosis.
- Clinical/Ancillary Labs
V. Classification of Severity
- Uncomplicated Malaria: No severe features or organ involvement.
- Severe/Complicated Malaria: Defined by WHO criteria:
VI. Management and Drug Therapy
A. Principles of Management
- Rapid diagnosis and treatment commencement
- Supportive care tailored to severity
- Drug regimens suited to Plasmodium species, resistance profile, and clinical scenario.
B. Antimalarial Drug Classes
| Drug/Class | Target Stage | Key Regimens/Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Artemisinin derivatives | Blood (as ACT) | Artesunate, artemether, DHA |
| Quinolines | Blood/hypnozoite | Chloroquine, mefloquine, quinine, primaquine |
| Atovaquone-Proguanil | Blood/liver | Malarone |
| Sulfadoxine-Pyrimethamine | Blood (partner drug) | SP (still used in IPTp) |
| Tetracyclines | Blood (partner drug) | Doxycycline, clindamycin (children/pregnancy) |
First-Line Therapies: Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapies (ACTs)
- Artemether-lumefantrine, artesunate-mefloquine, DHA-piperaquine, artesunate-amodiaquine, artesunate-SP.
- Rapid parasite clearance, efficacy against resistant P. falciparum.
- Administered orally, except IV artesunate for severe malaria.
Non-ACT options (species/region specific):
- Chloroquine (if no resistance for P. vivax, some non-Africa regions)
- Quinine (IV for severe malaria, oral for areas lacking IV artesunate)
- Atovaquone-proguanil (prophylaxis, alternative therapy)
- Mefloquine (prophylaxis, treatment, caution for neurotoxicity)
- Primaquine (radical cure for P. vivax/P. ovale; G6PD testing required)
- Doxycycline/clindamycin (used with quinine or artesunate for severe malaria, or as partner in ACTs; clindamycin preferred in children/pregnancy).
Severe Malaria Management
- IV artesunate is globally preferred over quinine.
- Supportive measures: Correct hypoglycemia, manage fluid/electrolytes, renal support as needed, seizure control, monitor for respiratory distress.
- Exchange transfusion very rarely, for extreme parasite burden.
Special Groups
- Pregnant women: Quinine + clindamycin or ACT, dependent trimester and local guidelines (avoid atovaquone, primaquine).
- Children: Lower thresholds for severe malaria, higher risk; careful monitoring for complications.
- Comorbid diseases (HIV, TB): Account for potential drug interactions.
To learn about the pharmacology of individual drug classes, please refer to this page.
VII. Prevention
A. Vector Control
- Insecticide-treated bed nets (ITNs), indoor residual spraying (IRS).
B. Chemoprophylaxis
- Travelers: Atovaquone-proguanil, doxycycline, mefloquine, and chloroquine (if susceptible region).
- Intermittent Preventive Therapy (IPT): In pregnancy (IPTp), children (IPTi), and infants.
C. Vaccines
- RTS,S/AS01 vaccine: Shown efficacy in children (pilot phase in Africa); ongoing research into broader/more durable vaccines.
D. Personal Protective Measures
- Mosquito avoidance: repellents, clothing, behavior adjustment.
VIII. Drug Resistance
- Chloroquine resistance: Widespread, especially for P. falciparum.
- Artemisinin resistance: Regions of Southeast Asia (K13 mutations, slower clearance), actively monitored worldwide.
- Other resistance: Mefloquine, SP, emerging resistance to ACT partner drugs. Combination therapy crucial for slowing resistance.
IX. Monitoring and Follow-up
- Continue daily blood smears for hospitalized or severe cases to monitor parasite clearance.
- Monitor for relapse in *P. vivax/P. ovale (risk of hypnozoites).
- Supportive lab monitoring (CBC, renal/liver function, glucose, acid-base status).
- Watch for side effects: hemolytic crisis (primaquine), neuropsychiatric symptoms (mefloquine), GI upset (ACTs), allergic reactions.
X. Complications
- Cerebral malaria (ICU care, seizure management)
- Severe anemia (transfusion)
- Acute kidney injury (renal replacement therapy)
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (supportive care)
- Hypoglycemia (especially in children with quinine, artesunate therapy)
- Splenic rupture, shock, bleeding disorders
- Hyperparasitemia (>10% RBCs).
XI. Summary Table: Drug Choices by Scenario
| Situation/Species | First-line | Alternatives/Adjuncts |
|---|---|---|
| Uncomplicated P. falciparum | ACTs | Atovaquone-proguanil, quinine |
| Severe malaria | IV artesunate | IV quinine (where artesunate unavailable) |
| Uncomplicated P. vivax/P. ovale | Chloroquine (+ primaquine for radical cure, G6PD tested) | ACTs where chloroquine resistance |
| Pregnancy (uncomplicated) | Quinine + clindamycin (first trimester); ACTs (after first) | Mefloquine (where permitted) |
| Prophylaxis (travelers) | Atovaquone-proguanil, doxycycline, mefloquine | Chloroquine (susceptible regions) |
| Relapse prevention | Primaquine (after G6PD test) | Tafenoquine (where available, G6PD tested) |
References
- Shrestha J, Malaria. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- WHO guidelines for malaria. World Health Organization. 2021, updated Sept 2025.
- Hunsicker LG. The Pharmacology of Antimalarials: A Rational Approach to the Therapy of Resistant Falciparum Malaria. Arch Intern Med. 1969;123(6):645–649.
- Mayo Clinic. Malaria: Diagnosis & treatment. Updated 2023 Feb.
- CDC. General Approach to Treatment | Malaria. 2025 May.
- WHO. New and updated malaria guidance. 2025.
- Malaria Journal. Assessing fitness costs in malaria parasites: implications for drug resistance management. 2025 Feb.
- Tandfonline. A systematic review on malaria and dengue vaccines. 2024 Apr.
Malaria
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.