Main Takeaway: A P-drug is a prescriber’s personal choice of first-line medicine for a specific indication, selected through a systematic and evidence-based process. Developing and maintaining a personal formulary of P-drugs streamlines decision-making, promotes rational therapeutics, and enhances patient safety.
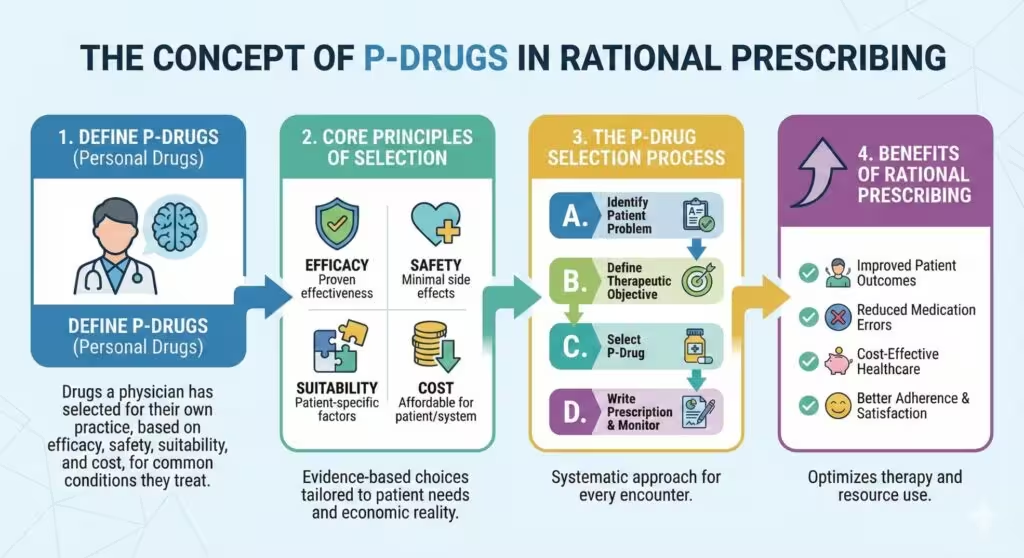
1. Definition and Purpose of P-Drugs
A P-drug (“personal drug”) is not merely the generic name of a medicine but encompasses:
- The drug substance itself
- The dosage form (e.g., tablet, injection)
- The dosage schedule (e.g., once daily)
- The duration of treatment
P-drugs serve as a clinician’s priority choices for given indications, reducing repetitive searches in daily practice and ensuring familiarity with each drug’s effects and side effects.
2. Relation to Essential Medicines and Guidelines
- Essential Medicines Lists (EMLs): National or WHO EMLs often contain dozens to hundreds of options; clinicians typically use only 40–60 drugs regularly. By selecting P-drugs from these lists, practitioners effectively create a personal essential medicines list tailored to their practice context.
- Standard Treatment Guidelines (STGs): Evidence-based STGs for common conditions should inform P-drug selection. P-drugs should align with STG recommendations while accounting for local availability, cost, and patient factors.
3. The Six-Step Process for Rational Prescribing
The WHO Guide to Good Prescribing outlines a six-step model, with P-drug selection comprising Step 3:
- Define the patient’s problem. Summarize diagnosis and relevant patient characteristics (e.g., comorbidities, allergies).
- Specify the therapeutic objective. Establish clear, measurable goals (e.g., reduce blood pressure to <140/90 mmHg).
- Choose and verify your P-drug:
a. Select a P-drug for the indication (Step 3a).
b. Verify its suitability for this patient (Step 3b)—check for contraindications, interactions, and patient-specific factors. - Write the prescription. Include drug name, dose, schedule, and duration.
- Provide information to the patient: instructions and warnings.
- Monitor effectiveness and adverse effects; adjust or stop treatment as needed.
4. Criteria for Selecting P-Drugs (The STEP Framework)
When comparing drug options, apply the STEP criteria:
- Safety: Evaluate adverse-effect profiles and contraindications.
- Therapeutic efficacy: Assess evidence of clinical benefit.
- Economy (cost): Consider affordability and cost-effectiveness.
- Propriety (suitability): Account for patient convenience, formulation, dosing schedule, and special conditions (e.g., pregnancy).
Example: Selecting a P-Drug for Acute Amoebic Dysentery
Among nitroimidazoles, tinidazole may be preferred over metronidazole due to similar efficacy and cost but greater suitability (shorter course, once- or twice-daily dosing).
5. Benefits of a P-Drug Formulary
- Efficiency: Reduces time spent reviewing alternatives for routine cases.
- Familiarity: Clinician expertise with P-drugs improves recognition of expected effects and adverse reactions.
- Consistency: Supports standardized prescribing practices within and across healthcare teams.
- Rationality: Mitigates impulsive or non-evidence-based choices influenced by marketing or habit.
By systematically selecting and regularly reviewing P-drugs according to these principles, prescribers establish a robust foundation for safe, effective, and cost-conscious patient care.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.

