Posted inmiscellaneous Pharmacology
Pharmacology of Magnesium Sulfate
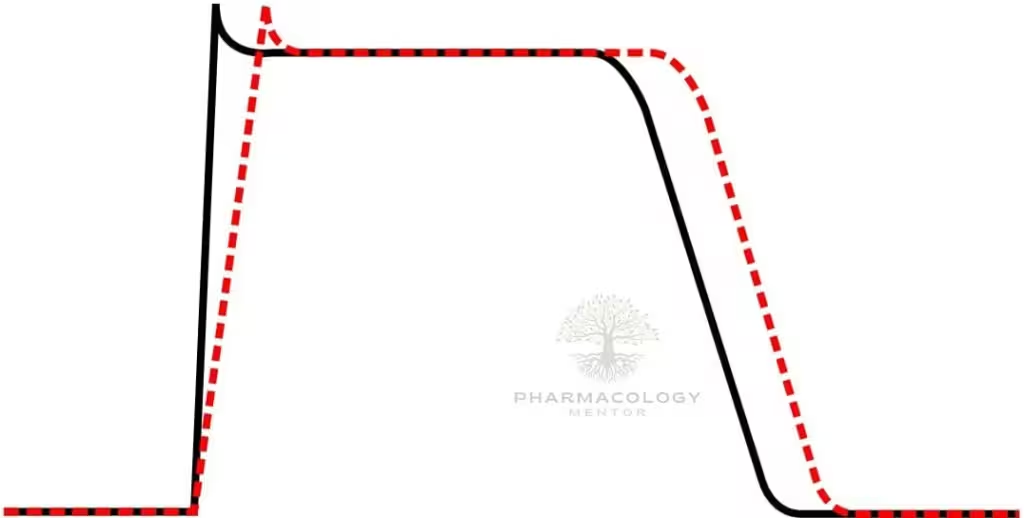
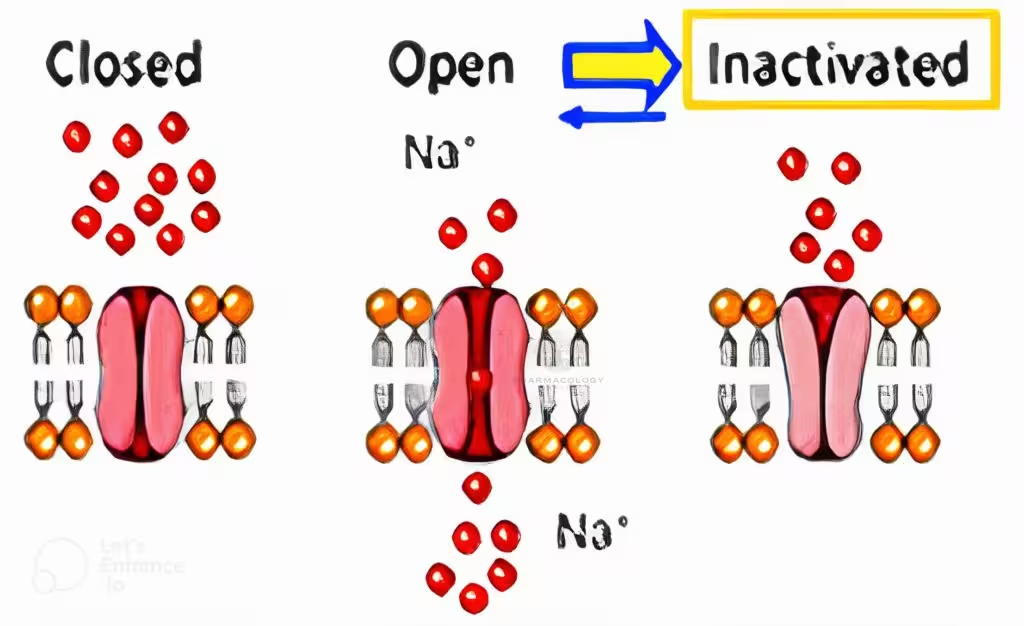
Introduction Magnesium is the fourth most abundant cation in the human body and plays a critical role in numerous physiological processes. Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) is an inorganic salt that has…