Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors are first‑line oral agents for erectile dysfunction that augment the endogenous nitric oxide–cGMP pathway in the corpus cavernosum to facilitate erection with sexual stimulation, and the class includes sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil, and avanafil. Standard pharmacology texts detail shared mechanisms with clinically important differences in onset, duration, food effects, selectivity, and interactions that guide individualized drug choice and safe use in practice.
Mechanism and physiology
Penile erection is initiated by parasympathetic release of nitric oxide (NO), activation of soluble guanylyl cyclase in trabecular smooth muscle, and generation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) that lowers intracellular calcium to cause relaxation and arterial inflow with venous occlusion. PDE5 localized in cavernosal smooth muscle hydrolyzes cGMP and terminates erection; PDE5 inhibitors competitively block cGMP catabolism, amplifying NO signaling so erection occurs only in response to sexual stimulation. Selectivity for PDE5 over other phosphodiesterase isoforms explains class effects and adverse‑effect profiles, such as PDE6 cross‑inhibition in retinal photoreceptors (visual tinge with sildenafil) and PDE11 inhibition in skeletal muscle (myalgia with tadalafil).
Classification and agents
- Sildenafil: prototypical PDE5 inhibitor, immediate‑release, variable food effect, and moderate duration of action.
- Vardenafil: close to sildenafil in kinetics and food effect, with similar clinical profile.
- Tadalafil: longer half‑life enabling once‑daily use; minimal food effect and additional approval for lower urinary tract symptoms in benign prostatic hyperplasia.
- Avanafil: more selective PDE5 blockade with rapid onset and shorter duration designed for on‑demand use.
Molecular pharmacology
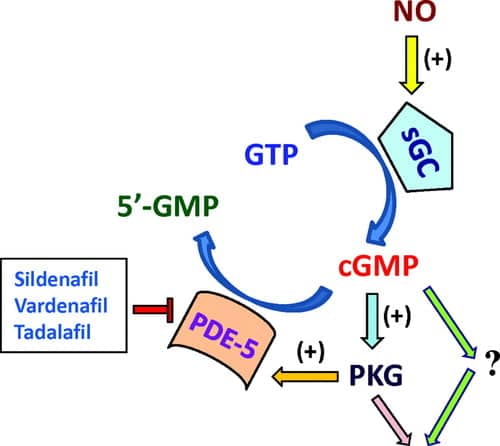
All agents competitively occupy the catalytic site of PDE5, protecting cGMP from hydrolysis and enhancing protein kinase G–mediated phosphorylation that reduces calcium, deactivates myosin light‑chain kinase, and relaxes cavernosal smooth muscle. The pharmacodynamic requirement for intact NO release means response is blunted in severe neurogenic or endothelial impairment, and coadministration with exogenous nitrates produces synergistic vasodilation and hypotension.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: sildenafil and vardenafil reach peak levels in about 1 hour and are delayed by high‑fat meals, while avanafil peaks within 30–45 minutes and tadalafil in 2 hours with less food effect.
- Distribution and metabolism: all are highly protein bound, extensively metabolized by CYP3A4 (with minor pathways via CYP2C9 for sildenafil/vardenafil), and have active metabolites of limited clinical significance except where CYP interactions alter exposure.
- Elimination: half‑lives are approximately 4–5 hours for sildenafil and vardenafil, about 17.5 hours for tadalafil, and around 5 hours for avanafil, determining dosing windows and daily versus on‑demand strategies.
Indications
- Erectile dysfunction: on‑demand or once‑daily regimens improve International Index of Erectile Function scores across vascular, psychogenic, diabetic, and post‑prostatectomy ED etiologies, with diminished response in severe neuropathy or advanced diabetes.
- Additional approvals: sildenafil and tadalafil are approved for pulmonary arterial hypertension at distinct dosing regimens, and tadalafil is approved for LUTS due to BPH, reflecting smooth muscle relaxant actions beyond cavernosal tissue.
Dosing (ED)
- Sildenafil: 25–100 mg taken about 1 hour before sexual activity; adjust based on efficacy and tolerability, avoiding more than once daily.
- Vardenafil: 10–20 mg about 1 hour before sexual activity with similar limits on frequency and high‑fat meal considerations.
- Tadalafil: 10–20 mg as needed 30–60 minutes before intercourse or 2.5–5 mg once daily for continuous effect and for ED with BPH symptoms.
- Avanafil: 50–200 mg 15–30 minutes before intercourse, favoring rapid, short‑window use.
Administration pearls
Instruct administration on an empty stomach for sildenafil and vardenafil when rapid onset is desired, allow adequate time to peak effect, and emphasize that sexual stimulation remains necessary for efficacy. Start with lower doses in hepatic impairment, with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, in older adults, and in those with hypotension or volume depletion, with careful titration to response.
Adverse effects
- Common and dose‑related: headache, flushing, nasal congestion, dyspepsia, and dizziness from systemic vasodilation are class effects and generally mild.
- Visual effects: transient blue–green color tinge and light sensitivity occur more with sildenafil due to PDE6 inhibition in retina; persistent vision loss is rare but NAION has been reported.
- Musculoskeletal: back pain and myalgia are more frequent with tadalafil, likely linked to PDE11 inhibition in skeletal muscle.
- Hearing: sudden sensorineural hearing loss is rare but a labeled precaution across the class.
- Cardiovascular: symptomatic hypotension and syncope can occur, especially with concomitant vasodilators, dehydration, or high starting doses.
- Priapism: prolonged erection beyond 4 hours requires urgent care to prevent ischemic injury.
Contraindications and cautions
- Absolute: any form of organic nitrate or nitric oxide donor coadministration due to profound, potentially life‑threatening hypotension from combined cGMP elevation.
- Riociguat: concurrent use with guanylyl cyclase stimulators is contraindicated for the same reason of excessive cGMP signaling and hypotension.
- Alpha‑blockers: risk of orthostatic hypotension is additive; use the lowest PDE5 inhibitor dose, ensure alpha‑blocker stability, and separate dosing when possible.
- Cardiovascular status: evaluate for unstable angina, recent myocardial infarction or stroke, severe hypotension, or uncontrolled hypertension before initiating therapy in line with safety principles.
Drug interactions
- CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, clarithromycin, ritonavir) increase PDE5 inhibitor exposure; start at the lowest dose or avoid per product‑specific guidance.
- CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin) may reduce efficacy by lowering plasma levels, sometimes necessitating alternative therapy.
- Alcohol and other vasodilators enhance hypotension and dizziness, warranting caution particularly with on‑demand higher doses.
- Aspirin and anticoagulants do not have direct pharmacokinetic interactions, but symptomatic hypotension can increase fall risk when combined with other agents.
Comparative features
Special populations and settings
- Diabetes and post‑prostatectomy ED: efficacy is lower on average, and optimization of comorbid risk factors plus rehabilitation strategies may be needed alongside PDE5 inhibitors.
- Hypogonadism: in men with low testosterone and suboptimal PDE5 inhibitor response, testosterone replacement can improve erectile outcomes when appropriately indicated and monitored.
- PAH and BPH: adhere to distinct dosing schedules and monitoring when using sildenafil or tadalafil for pulmonary arterial hypertension or tadalafil for LUTS/ED.
Clinical use and counseling
Set expectations that response requires sexual stimulation and may require several trials with correct timing and dose; instruct avoidance of grapefruit juice with certain agents, separation from alpha‑blockers, and absolute prohibition of nitrate co‑use. Discuss recognizing hypotension, visual or hearing changes, and priapism, and provide clear guidance on when to stop the drug and seek care.
Algorithmic selection
- Need fast onset and short window: consider avanafil for rapid use, or sildenafil/vardenafil with attention to food effect.
- Need long window or daily control (including LUTS): consider tadalafil PRN or daily based on preference and comorbidity profile.
- Prominent myalgia history: avoid tadalafil; prefer sildenafil or avanafil depending on onset needs.
- Concomitant strong CYP3A4 inhibitors: use reduced doses, prefer agents with product‑specific guidance for safe co‑use, or defer until interaction resolves.
High‑yield exam points
- PDE5 inhibitors enhance NO–cGMP signaling in corpus cavernosum, require sexual stimulation, and are contraindicated with all nitrates and riociguat.
- Differences across agents are clinically meaningful: tadalafil’s long half‑life enables daily ED and BPH dosing; sildenafil and vardenafil are slowed by high‑fat meals; avanafil achieves faster onset with higher selectivity.
- Class adverse effects are vasodilatory, with drug‑specific risks such as visual changes via PDE6 (sildenafil) and back pain via PDE11 (tadalafil), and rare but serious events include NAION, sudden hearing loss, and priapism.
References
- Ritter JM, Flower R, Henderson G, et al. Rang & Dale’s Pharmacology. 10th ed. London: Elsevier; 2024. Erectile dysfunction pharmacology and PDE5 inhibitors.
- Dhaliwal A, Moores C. PDE5 Inhibitors. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023–2025.
- Smith BP, Dillon KA. Sildenafil. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023–2025.
- Tai C, Carroll A. Tadalafil. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023–2025.
- Ahmed W, Zuo L. Phosphodiesterase 5: structure–function regulation and clinical translation. Pharmacol Res. 2021;170:105725.
- Fang Z, Yang Y. PDE5 inhibitors after nerve‑sparing radical prostatectomy: a meta‑analysis. Transl Androl Urol. 2020;9(6):2780–2793.
- Li H, Niu X. Testosterone plus PDE5 inhibitors vs monotherapy in hypogonadal men with ED: a meta‑analysis. Transl Androl Urol. 2020;9(2): 223–234.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.

awesome