I. Introduction
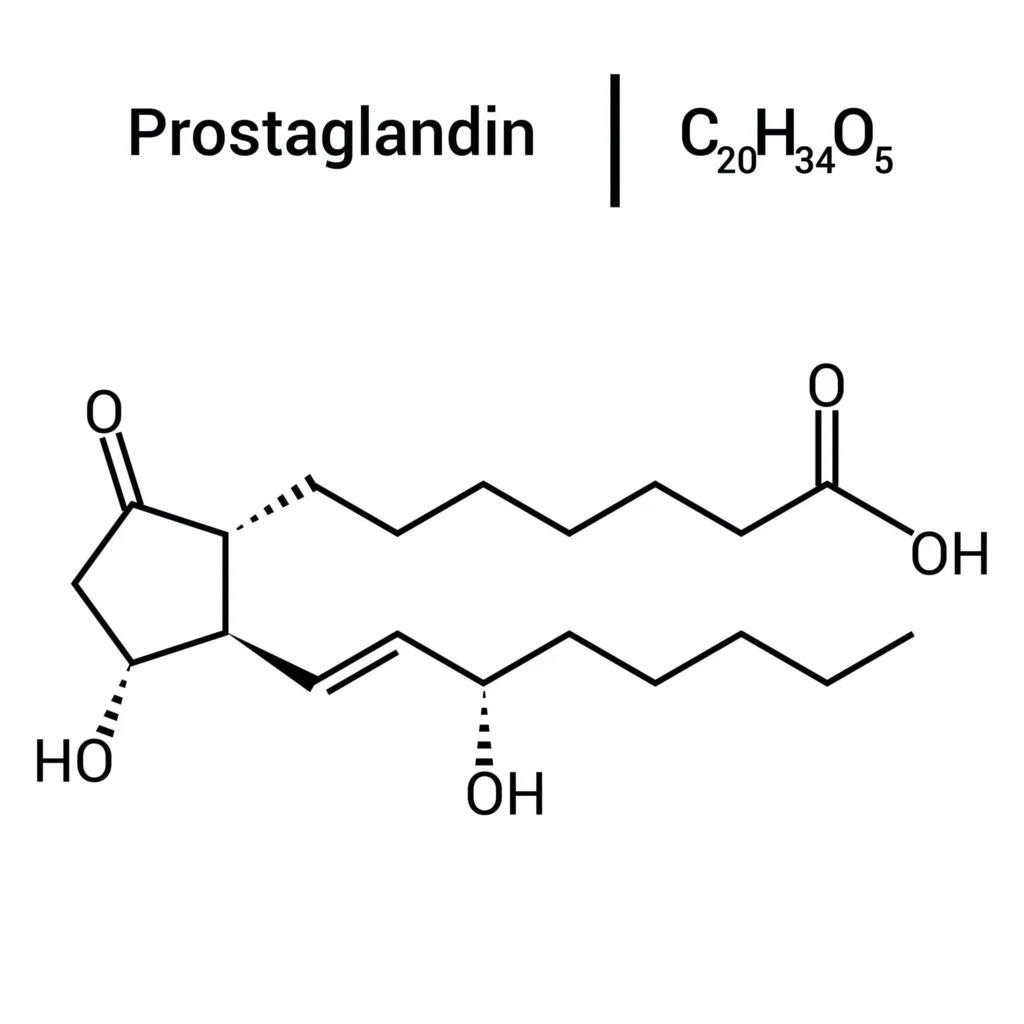
Prostaglandins are autacoids derived from arachidonic acid via the cyclooxygenase pathway and modulate numerous physiological processes—vascular tone, inflammation, gastric cytoprotection, uterine contraction, and intraocular pressure. Prostaglandin analogues are synthetic structural or functional mimetics designed to replicate or enhance one or more actions of natural prostaglandins, often with improved pharmacokinetics and receptor selectivity. Their clinical applications span from glaucoma and obstetric indications to peptic ulcer protection and pulmonary arterial hypertension.
II. Classification and Examples
| Subtype | Key Drugs | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| PGF2α analogues | Latanoprost, Bimatoprost, Travoprost, Tafluprost | Glaucoma |
| PGE1 analogues | Misoprostol, Alprostadil | Gastric protection, ED, ductus arteriosus patency |
| PGE2 analogues | Dinoprostone | Labor induction, cervical ripening |
| PGI2 analogues | Epoprostenol, Iloprost, Treprostinil, Beraprost | Pulmonary HTN, antiplatelet |
III. Mechanisms of Action
Prostaglandin receptors are G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) selectively activated by PG analogues, resulting in diverse tissue-specific effects:
- PGF2α analogues: Lower intraocular pressure via increased uveoscleral outflow (glaucoma therapy).
- PGE1/PGE2 analogues: Relax smooth muscle, modulate gastric mucosal protection, contract/relax uterine tissue depending on site/receptor.
- PGI2 analogues: Potent vasodilation in pulmonary vasculature; inhibit platelet aggregation.
IV. Pharmacological Profiles and Clinical Uses
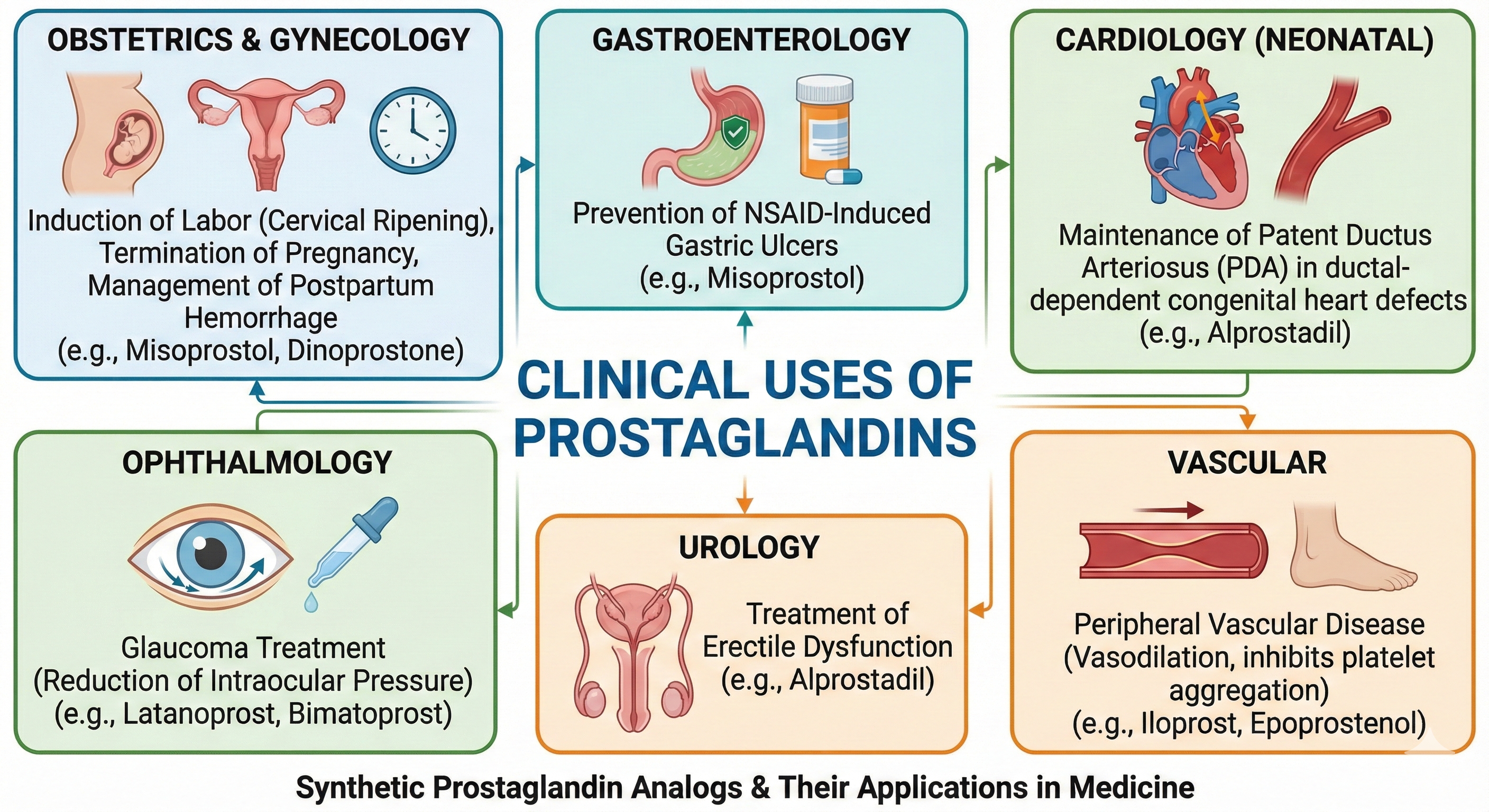
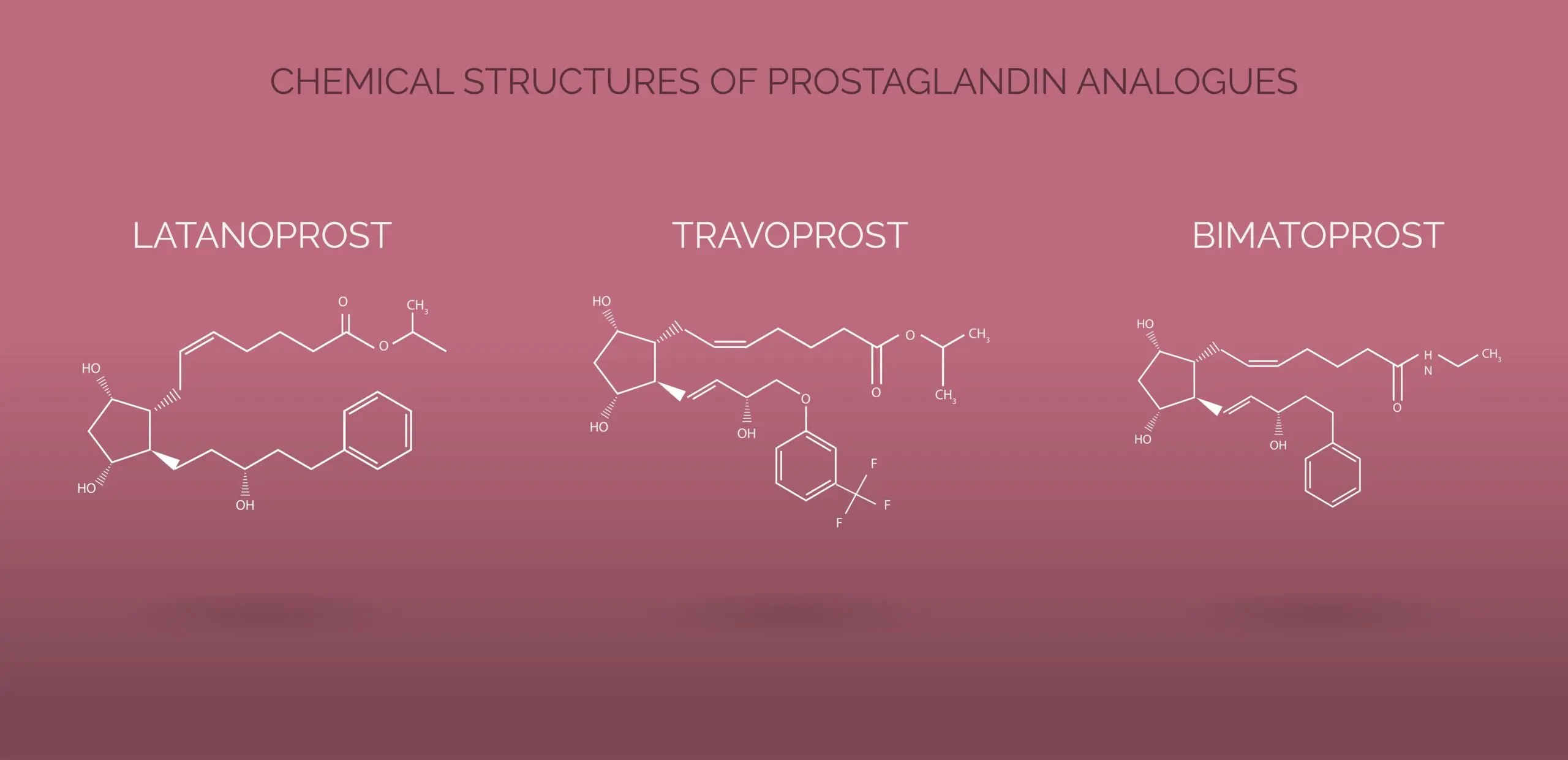
A. PGF2α Analogue Eye Drops (Glaucoma)
- Latanoprost, Bimatoprost, Travoprost, Tafluprost
Action: Topical application increases uveoscleral outflow of aqueous humor, lowering intraocular pressure (IOP).
Therapeutic use: Primary open-angle glaucoma; ocular hypertension
Pharmacokinetics: Administered once daily, well-absorbed into anterior segment.
Adverse effects: Iris pigment darkening, eyelash growth (hypertrichosis), conjunctival hyperemia, rare uveitis, cystoid macular edema.
Bimatoprost is also used for cosmetic eyelash enhancement.
B. PGE1 and PGE2 Analogues
1. Misoprostol (PGE1 analogue)
Action: Increases gastric mucus and bicarbonate production, reduces acid secretion.
Therapeutic use: Prevention of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers (co-prescribed with long-term NSAIDs), abortifacient use (with mifepristone).
Adverse effects: Diarrhea, abdominal cramps, uterine contractions, contraindicated in pregnancy (unless for medical abortion).
2. Alprostadil (PGE1 analogue)
Use:
- Maintains ductus arteriosus patency in neonates with congenital heart defects until surgery
- Erectile dysfunction (intracavernosal, intraurethral use)
Adverse effects: Penile pain, hypotension, flushing.
3. Dinoprostone (PGE2 analogue)
Use:
- Cervical ripening, induction of labor, pregnancy termination
Adverse effects: Uterine hyperstimulation, GI upset, fever.
C. PGI2 (Prostacyclin) Analogues
- Epoprostenol, Iloprost, Treprostinil, Beraprost
Action: Induce pulmonary/prostacyclin receptor-mediated vasodilation, inhibit platelet aggregation
Therapeutic use: Pulmonary arterial hypertension, Raynaud’s phenomenon, off-label for PVD
Pharmacokinetics: Epoprostenol (IV, short half-life), iloprost/treprostinil (inhaled, oral, subcutaneous, longer action)
Adverse effects: Flushing, headache, hypotension, jaw pain, limb pain
V. Other Indications
- Gemeprost and carboprost: Synthetic PGE1, PGF2α analogues, respectively; used in medical abortion and postpartum hemorrhage.
- Lubiprostone (PGE1 derivative): Activates ClC-2 chloride channels in gut, approved for chronic constipation and irritable bowel syndrome with constipation.
VI. Adverse Effects and Contraindications
| Drug/Class | Major Adverse Effects | Contraindications |
|---|---|---|
| Glaucoma agents | Iris/skin pigmentation, eyelash changes | Macular edema, uveitis risk |
| Misoprostol | Diarrhea, cramps, abortion risk | Pregnancy (unless intended) |
| Labor inducers | Uterine rupture, hyperstimulation | Prior C-section, uncontrolled asthma |
| Pulmonary HTN agents | Flushing, hypotension, bleeding | Cardiac decompensation, bleeding |
VII. Summary Table
| Analogue | Structure Base | Main Uses | Notable AE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latanoprost | PGF2α | Glaucoma | Iris pigment, lashes |
| Misoprostol | PGE1 | Ulcer prevention, abortion | Diarrhea |
| Dinoprostone | PGE2 | Labor, cervical ripening | Uterine hyperstim |
| Epoprostenol | PGI2 | Pulmonary hypertension | Flushing, headache |
Prostanoid receptors: transduction and functional cues
Therapeutic prostaglandin analogs: routes, uses, and key cautions
VIII. Key Learning Points
- Prostaglandin analogues are powerful and targeted modulators of smooth muscle and other tissues, harnessed in a range of therapies: glaucoma, GI protection, obstetrics, pulmonary hypertension, and more.
- Class and receptor selectivity defines both their main clinical utility and adverse effect profile.
- They have strict contraindications, especially in pregnancy and certain cardiovascular/eye conditions.
IX. References
- Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollmann BC. Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 13th Edition. “Prostaglandins and Leukotrienes.”
- Katzung BG, Trevor AJ, eds. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. 15th Edition. Chapters: Eicosanoids, Uterine relaxants/stimulants, Glaucoma pharmacology.
- Ritter JM, Flower RJ, Henderson G, et al. Rang & Dale’s Pharmacology. 10th Edition. GPCR ligands, glaucoma drugs, eicosanoid drugs.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.