Introduction
Diphenhydramine is a prototypical first-generation antihistamine with a long history of clinical use for allergic reactions, insomnia, motion sickness, and a variety of off-label applications. Its popularity in both prescription and over-the-counter preparations is a testament to its versatility, but its significant sedative and anticholinergic properties necessitate a deep understanding for safe and effective use.
This chapter examines diphenhydramine’s mechanisms, pharmacokinetics, therapeutic uses, adverse reactions, special populations, overdose management, and key drug interactions. Integration of classic textbook knowledge and contemporary evidence is provided for clinicians, educators, and advanced learners.
Chemical Structure and Classification
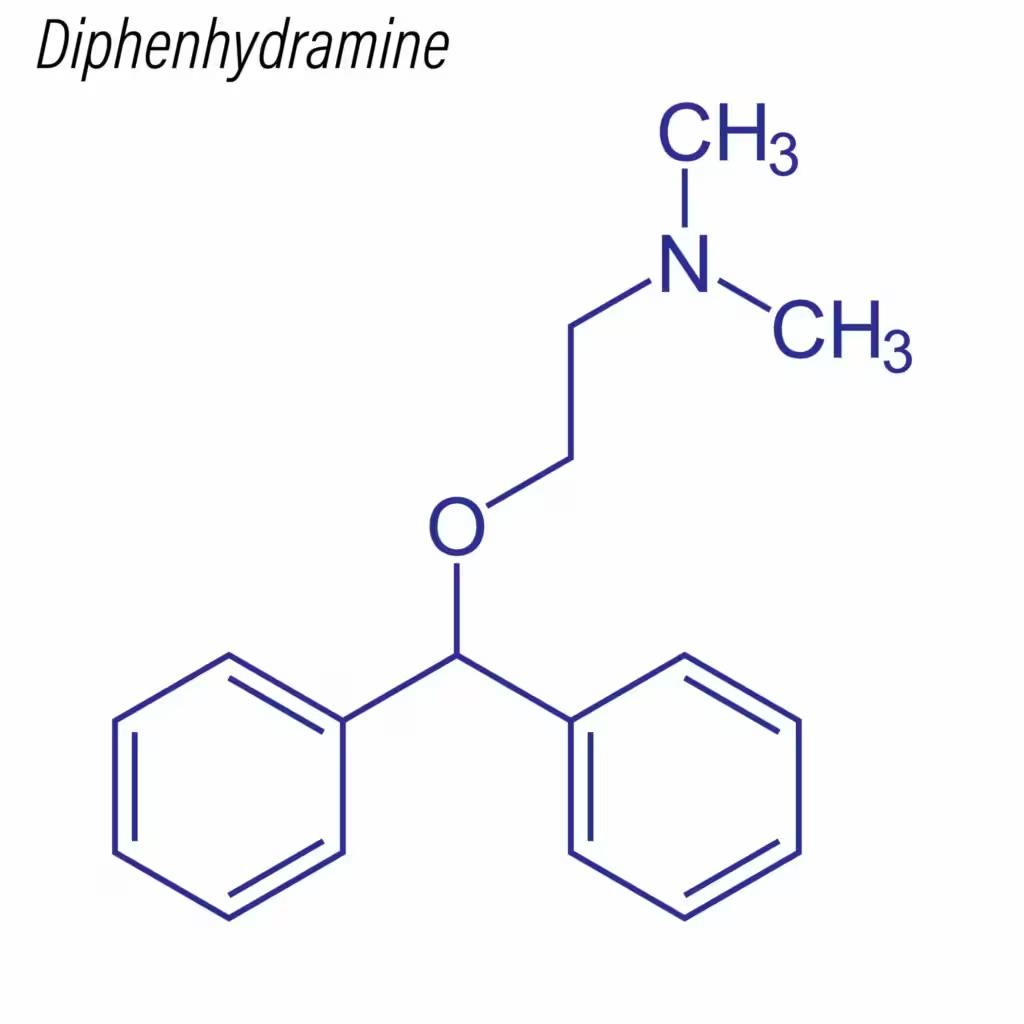
- Class: Ethanolamine derivative, first-generation H1-antihistamine.
- IUPAC name: 2-(Diphenylmethoxy)-N,N-dimethylethylamine hydrochloride.
- Physical Form: White crystalline powder, soluble in water.
Key Structural Features
- Unsubstituted side chain enhances CNS penetration (hence sedative effect).
- Non-selective due to low H1-receptor specificity versus later-generation antihistamines.
Mechanism of Action
1. H1-Receptor Antagonism (Inverse Agonism)
Diphenhydramine acts primarily as a competitive antagonist (more precisely, an inverse agonist) at the histamine H1 receptor:
- Histamine H1 Receptor Actions:
- Promotes vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, bronchoconstriction, and sensory nerve stimulation.
- CNS histamine modulates wakefulness, cognition, and vestibular function.
- Diphenhydramine’s antagonism reverses these effects, reducing inflammation, vasodilation, and sensory symptoms—while inducing drowsiness via central H1 blockade.
2. Antimuscarinic (Anticholinergic) Activity
- Structurally similar to atropine, diphenhydramine blocks muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M1-M5), especially in the CNS:
- Accounts for sedative-hypnotic effects and peripheral anticholinergic adverse effects (dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary retention).
- Explains utility as an antiparkinsonian agent for drug-induced extrapyramidal syndromes.
3. Local Anesthetic and Sodium Channel Blockade
- Blocks neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels, stabilizing membranes:
- Produces local anesthetic action topically and contributes to anti-pruritic effects.
4. Antitussive Action
- Suppresses the cough center in the medulla via central H1 and antimuscarinic effects, albeit less potent than codeine or dextromethorphan.
Pharmacokinetics
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Absorption | Rapidly, completely absorbed orally |
| Bioavailability | High |
| Onset | 15–60 min (oral), 2–10 min (IV/IM) |
| Peak | ~2 hours (oral) |
| Distribution | Widely, including CNS (crosses BBB) |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP450: CYP2D6, CYP1A2, CYP2C9) |
| Elimination | Renal (as metabolites and unchanged) |
| Half-life | 3.4–9.2 hours (may increase in elderly, liver disease) |
Dosage Forms and Administration
- Routes: Oral (tablets, capsules, liquids), Intramuscular (IM), Intravenous (IV), Topical creams/lotions.
- Common Adult Doses:
- Allergic reactions: 25–50 mg PO/IM/IV every 4–6 hours.
- Insomnia: 25–50 mg PO at bedtime.
- Motion sickness: 25–50 mg PO 30 min before exposure, then every 4–6 hours.
- Antiparkinsonism: 25–50 mg PO/IV/IM 3–4 times daily.
- Maximum daily dose: 300 mg (adults); adjust in elderly, hepatic or renal impairment.
Therapeutic Indications
1. Allergy and Hypersensitivity
- Acute allergic rhinitis, urticaria, angioedema, conjunctivitis: Symptomatic relief of rash, edema, tearing, pruritus, sneezing.
- Anaphylaxis (adjunct): Not a substitute for epinephrine, but useful for secondary symptom control.
2. Insomnia
- Short-term use as a non-benzodiazepine hypnotic, exploiting its sedative antihistaminic and anticholinergic activity.
3. Motion Sickness/Nausea
- Prophylaxis and treatment of motion sickness; blocks CNS histamine and cholinergic pathways involved in vestibular signaling.
- Some use in vertigo and labyrinthine disorders.
4. Antitussive
- Reduces cough reflex sensitivity, especially for nonproductive coughs associated with allergic or URTI triggers.
5. Parkinsonism/Drug-Induced Extrapyramidal Symptoms
- Acute dystonic reactions, parkinsonism, especially related to antipsychotic-induced EPS.
6. Topical Uses
- Creams/lotions for local pruritus, insect bites, minor burns, or skin irritations.
Adverse Effects
Common (>10%):
- CNS: Sedation, drowsiness, dizziness, impaired coordination, fatigue.
- Anticholinergic: Dry mouth, blurred vision, tachycardia, constipation, urinary retention, dilated pupils.
- GI: Nausea, loss of appetite.
Less Common/Serious:
- Paradoxical excitation: Especially in children (insomnia, irritability, hallucinations, seizures).
- Confusion, delirium: High risk in elderly; can precipitate falls.
- Cardiac: QT prolongation, ventricular arrhythmias (with overdose/IV use).
- Allergic: Hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis (rare).
- Other: Photosensitivity, local tissue irritation (parenteral/topical).
Special Considerations and Cautions
Populations at Increased Risk
- Elderly: Marked risk for delirium, falls, anticholinergic burden (avoid for insomnia or allergies when possible).
- Children: Contraindicated <6 years; may cause excitation, hallucinations, toxicity.
- Glaucoma: May worsen angle-closure risk.
- Prostatic hyperplasia: Urinary retention risk.
- Cardiovascular disease, severe hypertension: Tachyarrhythmias, increased BP.
- Hepatic/renal dysfunction: Reduced clearance, higher toxicity risk.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to diphenhydramine or related compounds.
- Neonates, premature infants, breastfeeding mothers.
- Use as local anesthetic in oral mucosa in children (risk of seizures).
Overdose and Toxicity
Clinical Presentation
- Anticholinergic Syndrome: Dry, flushed skin, mydriasis, blurred vision, tachycardia, fever, decreased bowel sounds, urinary retention.
- CNS Excitation: Agitation, delirium, hallucinations, tremor, seizures.
- Cardiac: Prolonged QRS/QT, ventricular tachycardia, fibrillation.
- Rhabdomyolysis, respiratory depression, coma (severe cases).
Management
- Supportive Care: Airway, breathing, circulation, IV fluids if hypotensive.
- Activated Charcoal (if within 1–2 hours of ingestion).
- Benzodiazepines for agitation and seizures.
- Sodium Bicarbonate: For ventricular arrhythmias and QRS widening.
- Magnesium sulfate: For torsades de pointes (polymorphic VT).
- Physostigmine: Rarely, reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, may reverse delirium under critical care (with great caution—risk of bradycardia, seizures).
Prognosis: Excellent with early, aggressive supportive care; mortality rare with appropriate treatment.
Drug Interactions
- CNS Depressants (alcohol, sedatives, benzodiazepines, opioids): Additive sedation, respiratory depression.
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): Potentiated anticholinergic, CNS, and cardiovascular adverse effects.
- Other anticholinergics (TCAs, antipsychotics): Additive cognitive/confusional risk, especially in elderly.
- QT-prolonging agents: Additive risk for arrhythmias (e.g., antiarrhythmics, macrolide antibiotics).
- CYP2D6 inhibitors/inducers: May vary serum levels.
Comparative Clinical Tables
Table 1: First vs. Second Generation H1 Antihistamines
| Feature | First-Generation (Diphenhydramine) | Second-Generation (Cetirizine, Loratadine) |
|---|---|---|
| CNS Sedation | ++ | + / – |
| Anticholinergic | ++ | + / – |
| Bronchodilation | Mild | Minimal |
| Duration | Short (4–6h) | Long (12–24h) |
| BBB Penetration | Yes | Minimal |
| OTC availability | Yes | Yes |
| Uses | Allergy, sedation, motion sickness, EPS, cough | Allergy only |
Table 2: Common Diphenhydramine Doses by Indication
| Indication | Adult Dose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Allergic reaction | 25–50 mg Q4–6h PO/IV/IM | Max 300 mg/day |
| Insomnia | 25–50 mg PO, bedtime | Short-term only |
| Motion sickness | 25–50 mg PO, Q4–6h as needed | Prior to travel/exposure |
| EPS (parenteral) | 10–50 mg IV/IM | For acute dystonias |
| Pediatric (6–12 y) | 12.5–25 mg Q4–6h | Avoid if <6y |
Recent Guidelines and Evidence
- Major guidelines (e.g., American Academy of Allergy Asthma & Immunology, Beers Criteria) recommend second-generation agents as first-line for allergic rhinitis due to superior safety (less CNS/anticholinergic effect).
- Diphenhydramine use for insomnia or cough in elderly is not recommended due to delirium/fall risk.
- Still appropriate for acute allergic reactions, adjunctive anaphylaxis management, short-term motion sickness, acute dystonia from neuroleptics.
Patient Counseling Points
- Caution regarding drowsiness; avoid driving or operating heavy machinery.
- Avoid concurrent alcohol or sedating medications.
- Maintain hydration; anticipate and manage dry mouth or constipation.
- Monitor for paradoxical CNS effects in children or elderly.
- Use only as directed to avoid toxicity.
Summary
Diphenhydramine is a widely accessible, multipurpose first-generation antihistamine. Its historical significance in allergy management is challenged by newer, less sedating agents, but it continues to fill important clinical niches (sleep aid, motion sickness prophylaxis, adjunct treatment of acute dystonia/allergy). However, its anticholinergic and sedative side-effect profile limits its use—especially in the elderly, pediatric, and patients with chronic comorbidities. Awareness of dosing, risk factors for toxicity, and critical adverse effects is necessary to optimize safety in use.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13th Edition.
- Katzung BG, Trevor AJ. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 15th Edition.
- Rang HP, Dale MM, Ritter JM, Flower RJ, Henderson G. Rang & Dale’s Pharmacology, 9th Edition.
- DrugBank Online: Diphenhydramine profile.
- NCBI Bookshelf: Diphenhydramine monograph.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.

