Clindamycin is a semi-synthetic lincosamide antibiotic that exerts its antimicrobial action by binding to the 23S rRNA of the 50S ribosomal subunit, thereby inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis through blockage of peptide bond formation and interference with translocation. This results predominantly in a bacteriostatic effect, though bactericidal activity may be observed at higher concentrations against certain susceptible organisms.
Chemical Structure and Properties
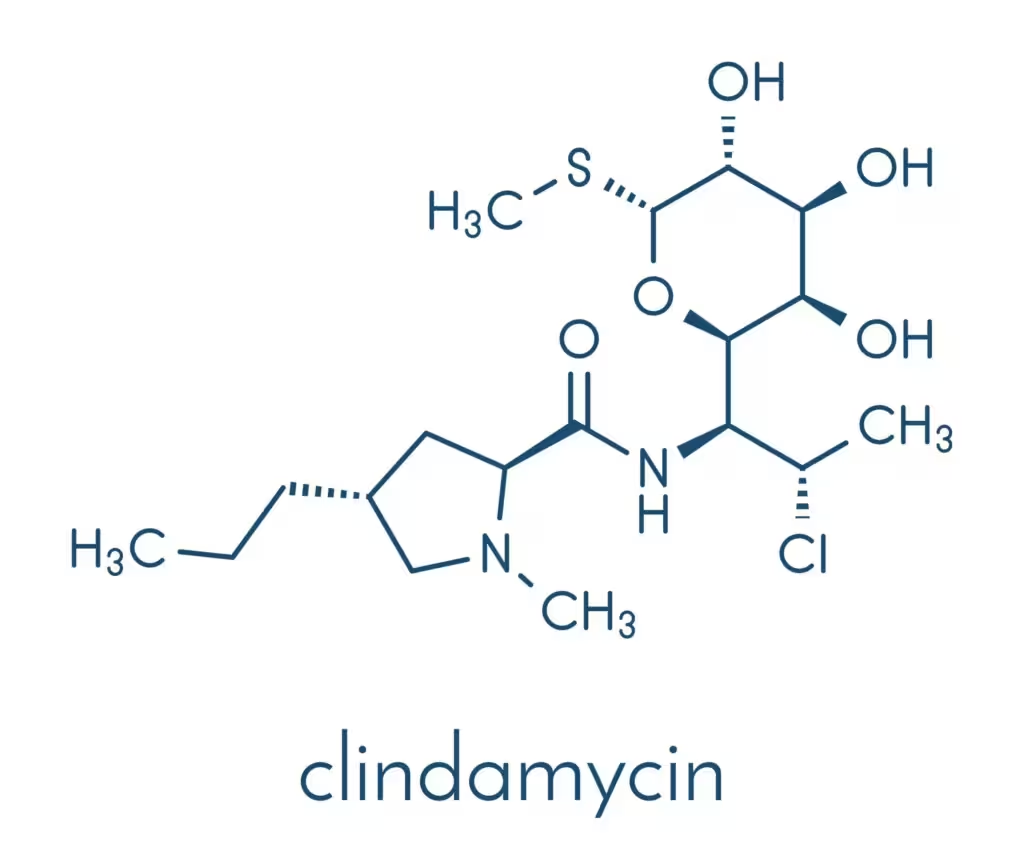
Clindamycin is chemically described as methyl 7-chloro-6,7,8-trideoxy-6-(1-methyl-trans-4-propyl-L-2-pyrrolidinecarboxamido)-1-thio-L-threo-α-D-galacto-octopyranoside. It is a semi-sy
Antimicrobial Spectrum
Clindamycin displays activity against many Gram-positive aerobes (including Streptococcus pyogenes, viridans group streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus— notably community-acquired MRSA where susceptible) and a wide range of anaerobes (especially above the diaphragm, such as Peptostreptococcus and Clostridium perfringens). However, its activity against Bacteroides fragilis group may be limited by regional resistance patterns. Clindamycin lacks intrinsic activity against Enterococcus, most Gram-negative aerobes, and Clostridioides difficile.
Pharmacokinetics
Clindamycin is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with ~90% bioavailability and peak plasma concentrations achieved in 45–60 minutes for oral doses. Oral absorption is unaffected by food. The drug is extensively distributed, including into tissues, abscesses, bone, and has high protein binding (~80–90%). Penetration into the CSF is poor, but concentrations in bone and tissues are adequate for most indications. Clindamycin undergoes hepatic metabolism (via CYP3A4/5) to active and inactive metabolites, and is primarily eliminated via the bile and, to a lesser extent, the urine. The elimination half-life is approximately 2–3 hours (can be prolonged in hepatic impairment or neonates).
Indications
- Skin and soft-tissue infections (cellulitis, abscess, some CA-MRSA) when susceptible
- Anaerobic infections above the diaphragm (aspiration pneumonia, lung abscess)
- Bone and joint infections (osteomyelitis) due to high bone penetration
- Dental and oral infections
- Pelvic inflammatory disease and postpartum endometritis (as part of multidrug regimens)
- Bacterial vaginosis (topical vaginal formulations) and acne vulgaris (topical)
- Adjunct therapy in necrotizing fasciitis and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome to inhibit toxin production
- Alternative for beta-lactam allergy in various susceptible infections
Dosing
- Adults (Systemic infections): 300–450 mg orally q6–8h for mild/moderate infections; 600 mg orally q8h or 600–900 mg IV q8h for severe infections (max 4.8 g/day)
- Pediatrics: 20–40 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6–8h
- Necrotizing fasciitis/toxin suppression: 900 mg IV q8h as adjunct
Adverse Effects
Common: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rash, abdominal pain, transient increase in liver enzymes.
Serious: High association with antibiotic-associated diarrhea and Clostridioides difficile infection (may cause severe or fatal colitis, which is reflected in a boxed warning), as well as rare hepatotoxicity, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, and hypersensitivity reactions.
Contraindications and Precautions
Contraindicated with prior hypersensitivity to clindamycin or lincomycin. Use cautiously in patients with histories of C. difficile infection or severe hepatic impairment, adjusting dosing interval as needed.
Drug Interactions
- Antagonism with macrolides may occur due to overlapping ribosomal targets
- Synergistic neuromuscular blockade with neuromuscular blockers—monitor with anesthesia
- CYP3A4 inhibitors (increase levels) and inducers (decrease levels) can affect metabolism
Resistance and D-Test
Resistance most commonly arises from methylation of the 23S rRNA target (erm genes), seen as inducible or constitutive resistance, which is detected with the D-test in Staphylococcus and beta-hemolytic streptococci. Efflux pump genes (msrA) and enzymatic inactivation (lnu) also occur. Local antibiograms guide empiric use for anaerobic infections and MRSA, as resistance rates can be region-specific.
Special Populations
- Pregnancy: Crosses placenta; generally considered safe when indicated
- Lactation: Present in breast milk; monitor infants for GI upset or thrush
- Hepatic impairment: May require extended dosing intervals and close monitoring
- Renal impairment: No adjustment typically needed, but caution with severe hepatic plus renal dysfunction
Monitoring
Monitor for new-onset or persistent diarrhea (promptly evaluate for C. difficile), and with prolonged therapy, monitor CBC and liver function.
Clinical Pearls
- Excellent oral bioavailability allows early IV-to-oral switch
- Effective for toxin suppression in invasive streptococcal/staphylococcal infections
- Topical combinations with benzoyl peroxide for acne reduce resistance
- Not recommended empirically for intra-abdominal infections in regions with high B. fragilis resistance
References
- Murphy PB, Adam GP, Stevenson B, et al. Clindamycin. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Feb 27.
- Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollmann BC, editors. Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 14th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2022.
- Katzung BG, Vanderah TW, editors. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. 16th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2021.
- Johns Hopkins ABX Guide. Clindamycin. Updated 2024 Dec 13.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.

