Introduction
Welcome to this all-encompassing guide to Diuretics and Antidiuretics. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, a student, or someone simply interested in pharmacology, this article is designed to help you understand these fascinating drug classes in brief (this is not a detailed overview). Let’s dive right in!
What Are Diuretics?
Diuretics are a class of medications commonly known as “water pills.” They help your body get rid of excess water and salt through urine. This process is crucial for treating various conditions like hypertension, heart failure, and edema.
Mechanism of Action
Diuretics work by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium ions in the kidneys. This action increases the osmotic pressure in the renal tubules, leading to increased urine production. The mechanism varies depending on the type of diuretic used.
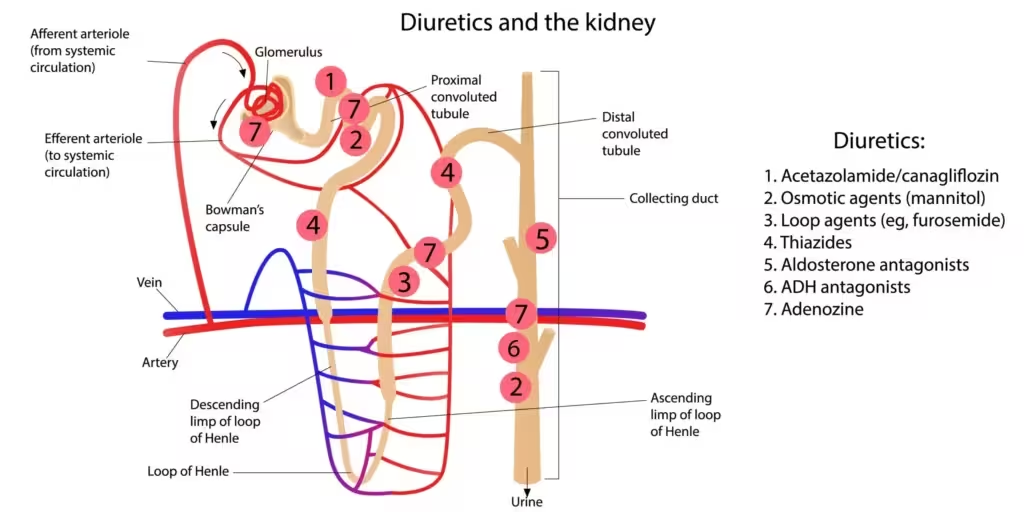
Types of Diuretics
There are several types of diuretics, each with its own unique mechanism and clinical applications. The main types include:
1. Loop Diuretics
- Mechanism of Action: Act on the ascending loop of Henle in the kidney to inhibit sodium, potassium, and chloride reabsorption.
- Examples: Furosemide (Lasix), Bumetanide (Bumex), Torsemide (Demadex)
- Clinical Use: Acute Heart failure, edema, hyperkalemia
2. Thiazide Diuretics
- Mechanism of Action: Act on the distal convoluted tubule to inhibit sodium and chloride reabsorption.
- Examples: Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), Chlorthalidone, Indapamide
- Clinical Use: Hypertension, mild heart failure, kidney stones
3. Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
- Mechanism of Action: Act on the collecting ducts to inhibit sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion.
- Examples: Spironolactone (Aldactone), Eplerenone (Inspra), Amiloride, Triamterene
- Clinical Use: Hypokalemia, heart failure, ascites in liver disease
4. Osmotic Diuretics
- Mechanism of Action: Increase the osmolarity of the filtrate, pulling water into the nephron.
- Examples: Mannitol, Isosorbide
- Clinical Use: Acute kidney injury, cerebral edema, glaucoma
5. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
- Mechanism of Action: Inhibit the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, reducing the reabsorption of bicarbonate.
- Examples: Acetazolamide (Diamox), Methazolamide
- Clinical Use: Glaucoma, altitude sickness, metabolic alkalosis
6. Combination Diuretics
- Mechanism of Action: Combine the effects of different types of diuretics for synergistic action.
- Examples: Dyazide (hydrochlorothiazide + triamterene), Aldactazide (spironolactone + hydrochlorothiazide)
- Clinical Use: Hypertension, edema, heart failure
What Are Antidiuretics?
Antidiuretics are agents that reduce urine production. They are often used to treat conditions like diabetes insipidus and nocturnal enuresis.
Mechanism of Action
Antidiuretics primarily work by increasing the reabsorption of water in the kidneys. This action is generally mediated through vasopressin receptors.
Types of Antidiuretics
The main types of antidiuretics include:
- Vasopressin Analogues: Such as desmopressin.
- Thiazide Diuretics: Ironically, low doses can have antidiuretic effects.
Clinical Uses
Antidiuretics are used for:
- Diabetes Insipidus: To control excessive urination.
- Nocturnal Enuresis: To manage bedwetting in children.
Side Effects and Precautions
Diuretics
Common side effects include dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and kidney dysfunction. Always consult a healthcare provider for proper dosing and monitoring.
Antidiuretics
Potential side effects include water intoxication and hyponatremia. Monitoring is essential.
Drug Interactions
Diuretics
Interactions can occur with antihypertensives, NSAIDs, and certain antibiotics.
Antidiuretics
Interactions may happen with antiepileptics and SSRIs.
Natural Alternatives
Herbal Diuretics
Examples include dandelion and green tea.
Herbal Antidiuretics
Examples are cranberry and saw palmetto.
FAQs
- What are the main differences between diuretics and antidiuretics?
- Diuretics increase urine production, while antidiuretics decrease it.
- Can diuretics be used for weight loss?
- Not recommended, as the weight loss is mainly water weight.
- Are there natural alternatives to antidiuretics?
- Yes, herbal options like cranberry can be effective, but consult a healthcare provider first.
- Do diuretics deplete potassium?
- Some types, like loop and thiazide diuretics can, but potassium-sparing diuretics do not.
- How long do the effects of antidiuretics last?
- It varies depending on the type and dosage.
- Can I take diuretics without a prescription?
- It’s not advisable due to potential side effects and interactions.
Conclusion
Understanding Diuretics and Antidiuretics Pharmacology is crucial for both healthcare professionals and the general public. These drugs have a wide range of applications but come with a set of precautions. Always consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.