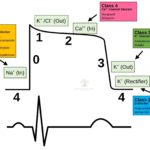
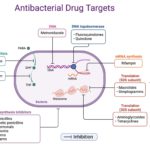
Pharmacology Definitions and Terminology
Pharmacology is the study of drugs and their interactions with living organisms. It encompasses various terms and concepts related to drug action, classification, and administration. Here are some common definitions and terms used in pharmacology: Drug: A chemical substance that interacts with the body to produce a physiological effect, either for therapeutic purposes, diagnostic purposes, … Read more