Antimicrobial resistance is a leading global health threat, characterized by the ability of microbes (bacteria, fungi, viruses, parasites) to withstand drugs formerly effective against them. The emergence and spread of AMR threatens the effectiveness of essential medical treatments, increases morbidity and mortality, and imposes substantial costs on healthcare systems and societies.
What is Antimicrobial Resistance?
AMR arises when microorganisms—bacteria (antibiotic resistance), viruses (antiviral resistance), fungi (antifungal resistance), and parasites (antiparasitic resistance)—evolve or acquire mechanisms to survive exposure to antimicrobial agents. This can occur via spontaneous genetic mutations or, more commonly, through the transfer of resistance genes among microbial populations.
Mechanisms of Resistance
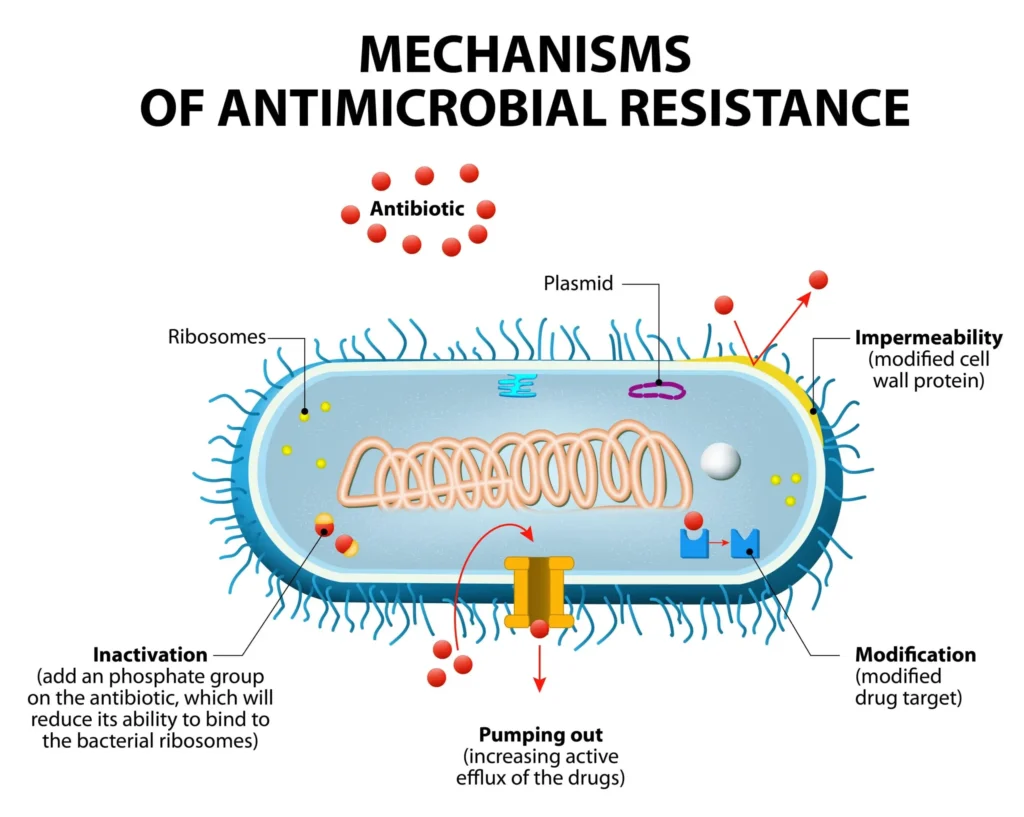
- Enzymatic drug inactivation or modification: Microbes produce enzymes (e.g., β-lactamases, carbapenemases) that degrade or alter the antimicrobial before it reaches its target.
- Alteration of drug targets: Mutations or enzymatic changes modify the binding site such that the drug can no longer interact effectively (e.g., modified penicillin-binding proteins, altered ribosomal RNA).
- Reduced drug accumulation:
- Efflux pumps actively extrude antimicrobials from the microbial cell.
- Decreased permeability: Altered porins or membrane changes impede antibiotic entry.
- Bypass pathways: The microbe activates alternative metabolic pathways that bypass the inhibited target.
- Biofilm formation: Bacteria within biofilms are shielded from drugs and host defenses, greatly increasing their resistance.
- Resistance can be intrinsic (naturally occurring in certain species) or acquired (via mutation or horizontal gene transfer).
Factors Driving Antimicrobial Resistance
- Misuse and overuse of antimicrobials: Inappropriate prescription, patient non-adherence, and use in viral/non-bacterial infections.
- Agricultural and veterinary use: Antibiotics are commonly used as growth promoters and prophylactics in animals, promoting resistance that can be transferred to human pathogens.
- Environmental contamination: Inappropriate disposal of drugs and animal waste containing antimicrobials facilitates resistance gene propagation.
- Poor infection control, inadequate sanitation, and lack of rapid diagnostics further exacerbate spread.
Global Burden and Impact
- WHO and CDC cite AMR as one of the most critical public health threats of the 21st century.
- Estimated ~5 million annual deaths are associated with resistant infections; projections warn of up to 10 million deaths annually by 2050 if trends continue.
- AMR renders common infections and routine medical procedures (surgeries, chemotherapy) significantly riskier.
- MDR “superbugs” (e.g. MRSA, VRE, carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales, pan-resistant gonorrhea, multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis) are increasingly prevalent and difficult to treat.
Global and National Responses
- WHO Global Action Plan (2015): Five pillars—improve awareness, strengthen surveillance, reduce infection incidence, optimize antimicrobial use, invest in new interventions and research.
- Antimicrobial stewardship: Programs and policies in healthcare aim to optimize therapy, minimize unnecessary use, and reduce the spread of resistance.
- Surveillance and One Health initiatives: Integrated monitoring in humans, animals, and the environment.
Key Examples of Mechanisms and Resistance:
| Mechanism | Example |
|---|---|
| Enzyme inactivation | β-lactamases degrade penicillins |
| Target alteration | MRSA alters penicillin-binding proteins (PBP2a) |
| Efflux pumps | Pseudomonas aeruginosa multidrug efflux |
| Reduced permeability | Carbapenem resistance in Gram-negatives (porin loss) |
| Biofilm formation | Chronic Pseudomonas infections in CF |
Preventive Measures
- Use antimicrobials judiciously—prescribe only when necessary, for the right duration and spectrum.
- Promote infection prevention—hand hygiene, vaccination, sanitation.
- Develop rapid diagnostics and new antimicrobials.
- Public and professional education.
References
- Habboush Y, Guzman N. Antibiotic Resistance. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- World Health Organization. Implementing the global action plan on antimicrobial resistance. WOAH, 2024.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About Antimicrobial Resistance. CDC; 2025 Jan 30.
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 14th ed. McGraw-Hill; 2022.
- Belay WY et al. Mechanism of antibacterial resistance, strategies and next-generation approaches. Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 15.
- Medlicott K. Global Action Plan to combat antimicrobial resistance. WHO; 2021.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.

