Overview and Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you should be able to:
- Describe the chemical origin, classification, and electrophysiologic actions of quinidine.
- Explain its pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and characteristic ECG effects.
- Identify evidence-based indications, dosing strategies, monitoring, and contraindications.
- Recognize common and serious adverse effects, major drug–drug interactions, and toxicity management.
- Compare quinidine with related Class IA antiarrhythmics and outline its role in contemporary practice.
Quinidine is a prototypical Class IA antiarrhythmic historically used in atrial and ventricular arrhythmias. Although its use has declined due to proarrhythmic risk and the emergence of better-tolerated alternatives, it remains an instructive archetype for understanding sodium channel–blocking drugs that also prolong repolarization. Select niche roles persist, particularly where its unique ion-channel profile offers benefit. [1–4]
Historical Perspective, Source, and Chemistry
- Origin: Quinidine is a stereoisomer of quinine, both alkaloids derived from the bark of Cinchona species (“Peruvian bark”). It was introduced early in the 20th century for arrhythmia suppression after observations of quinine’s cardiac effects. [1,3]
- Structure/activity: As a Class IA agent, quinidine exhibits a moderate rate-dependent block of fast inward sodium channels (Nav1.5) coupled with blockade of multiple repolarizing potassium currents (notably IKr), and it possesses antimuscarinic and mild alpha-adrenergic antagonism. These properties underlie its mixed electrophysiologic signature—slowed conduction with prolonged refractoriness and action potential duration (APD). [1–3]
Classification and Mechanism of Action
- Vaughan Williams: Class IA antiarrhythmic. [2,3]
- Primary actions:
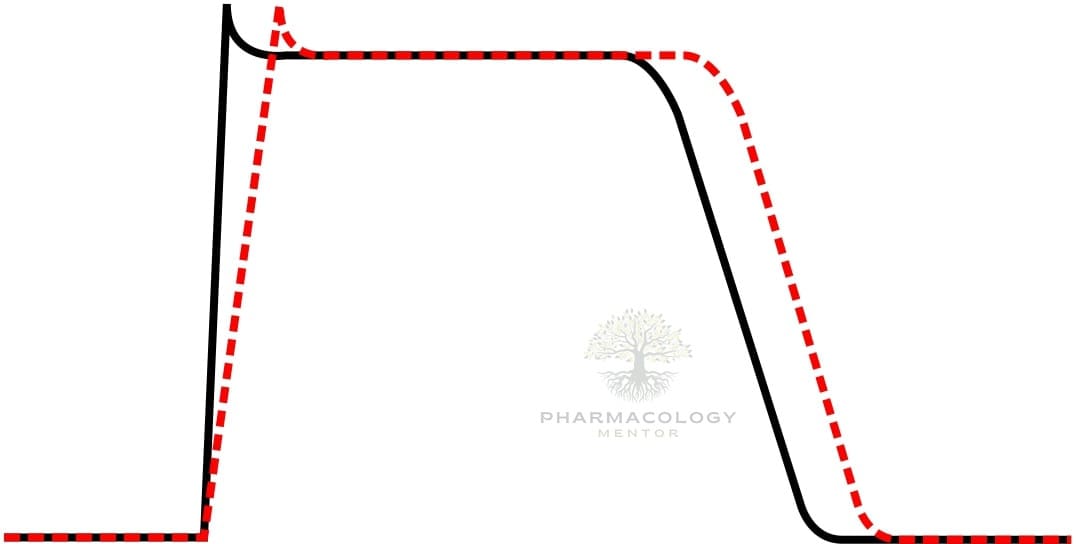
- Na+ channel block (phase 0): Moderate depression of Vmax in atrial, ventricular, and Purkinje fibers, slowing conduction and widening QRS, with use-dependence (more effect at higher rates). [1–3]
- K+ channel block (phase 3): Prolongs APD and effective refractory period (ERP) via IKr inhibition, contributing to QT prolongation. [1,2]
- Decreased automaticity: Reduces slope of phase 4 depolarization, suppressing ectopic pacemakers; increases diastolic threshold of excitability. [1,3]
- Antimuscarinic effects: Can facilitate AV nodal conduction (increased ventricular response) in atrial flutter/fibrillation unless an AV nodal blocker is co-administered. [2,3]
- Alpha-adrenergic antagonism: Mild peripheral vasodilation; IV administration can precipitate hypotension. [1,2]
- Tissue selectivity and use-dependence:
- Greater effects in fast-response tissues (His-Purkinje, ventricular myocardium) versus nodal tissues.
- Enhanced Na+ channel block at faster heart rates and in depolarized ischemic tissue. [1–3]
Key ECG effects:
- PR: may increase (conduction slowing) or remain unchanged.
- QRS: increases (Na+ block).
- QTc: increases (IKr block), correlating with torsades risk. [1–3]
Electrophysiologic Consequences by Arrhythmia Substrate
- Atrial flutter/fibrillation (AF): Slows atrial conduction and prolongs atrial refractoriness; antimuscarinic action may paradoxically increase AV nodal conduction, risking rapid ventricular rates without prior AV node blockade. [2,3]
- Reentry circuits: Slows conduction and increases ERP, potentially terminating reentry or preventing its reinitiation. [1,2]
- Ventricular ectopy/VT: Suppresses automatic foci and may interrupt reentrant VT; caution due to proarrhythmic risk (torsades de pointes). [1–3]
- Accessory pathways: Class IA agents can modify conduction across bypass tracts; however, safer and more predictable alternatives exist in acute pre-excited AF. [2]
Pharmacokinetics
- Formulations: Oral salts (e.g., quinidine sulfate immediate-release [IR] and extended-release [ER]; quinidine gluconate ER). Many traditional brands are discontinued in several markets; availability can be limited. [1,2]
- Absorption: Well absorbed orally; bioavailability typically moderate to high (reduced by first-pass metabolism and formulation differences). Food may mitigate GI adverse effects. [1,2]
- Distribution: Extensive tissue distribution (apparent Vd roughly a few L/kg); protein binding is substantial. [1–3]
- Metabolism: Predominantly hepatic via CYP3A4 to active and inactive metabolites (e.g., 3-hydroxyquinidine). Quinidine is a strong CYP2D6 inhibitor and a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitor. [1,2]
- Elimination: Mixed hepatic and renal routes; a fraction excreted unchanged in urine. Elimination half-life is on the order of several hours (commonly cited in the 6–8 h range), prolonged with hepatic impairment, heart failure, or reduced clearance. [1–3]
- Therapeutic plasma concentrations: Target range often cited around 2–6 micrograms/mL; toxicity becomes more likely at higher levels. Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) enhances safety given narrow index. [1,2]
- Pharmacogenomics and transporters:
- Strong inhibition of CYP2D6 can phenoconvert normal metabolizers to functional poor metabolizers for 2D6 substrates. [1,2]
- P-gp inhibition explains major interactions (e.g., digoxin). [1]
Clinical implications:
- Dose reductions or extended dosing intervals are prudent in hepatic dysfunction; consider cautious adjustment in significant renal impairment.
- Monitor trough levels after steady state (≥3–5 half-lives), after dose changes, and when adding/removing interacting drugs. [1,2]
Pharmacodynamics and ECG Monitoring
- Dose-related increases in QRS and QTc necessitate serial ECGs:
- QRS widening >25% from baseline suggests excessive Na+ channel block; consider dose reduction or discontinuation.
- QTc >500 ms or an increase >60 ms from baseline confers heightened torsades risk; correct electrolytes, reevaluate therapy. [1–3]
- Maintain serum potassium and magnesium in the high-normal range to mitigate proarrhythmia. [1–3]
Indications and Clinical Use
Contemporary use is limited due to proarrhythmic risk and availability of safer agents. Nonetheless, key indications include:
- Atrial fibrillation/flutter:
- Rhythm control (pharmacologic cardioversion and maintenance) historically; now largely supplanted by Class IC agents (in structurally normal hearts) or amiodarone/dofetilide/sotalol, given quinidine’s adverse profile. If used, pre-treat with an AV nodal blocker (e.g., beta-blocker or non-DHP CCB) to avoid 1:1 flutter conduction. [1–3]
- Ventricular arrhythmias:
- Suppression of symptomatic, non–life-threatening ventricular ectopy or sustained VT historically; today, generally reserved for select cases under specialist care when alternatives are unsuitable. [1–3]
- Inherited arrhythmia syndromes (selected off-label scenarios):
- Brugada syndrome: Quinidine’s block of Ito and IKr may reduce ventricular arrhythmias in patients with recurrent ventricular fibrillation or frequent ICD shocks when other options are limited. This role is described in advanced texts and specialty literature; use requires expert oversight. [1,3]
- Short QT syndrome: Can prolong QT and increase refractoriness in some genotypes, under specialized care. [1]
- Other uses (non-cardiac, low-dose):
- Quinidine is co-formulated at low dose with dextromethorphan for pseudobulbar affect to inhibit CYP2D6 and raise dextromethorphan exposure; this is distinct from its antiarrhythmic application and uses much lower quinidine doses. [1,2]
Bottom line: In many settings, guideline-preferred rhythm-control strategies have displaced quinidine; its use is now largely niche and specialized. [1–3]
Dosing and Administration
Note: Specific product availability and base-equivalent dosing vary by salt and market; consult local product information.
- Atrial fibrillation/flutter (conversion/maintenance):
- IR dosing often initiated at modest doses (e.g., 200–400 mg PO every 6 hours), with cautious uptitration guided by ECG and serum levels. ER formulations may be dosed every 8–12 hours. [1,2]
- Always pair with rate control initially (beta-blocker or non-DHP CCB) to mitigate accelerated AV conduction. [2]
- Ventricular arrhythmias:
- Similar total daily doses divided q6–8h (IR) or q8–12h (ER); titrate to effect, tolerability, and therapeutic plasma concentrations. [1,2]
- Dose adjustments:
- Hepatic impairment: reduce dose and intensify monitoring.
- Renal impairment: consider reduction if significant, monitor levels.
- Elderly/frail: start low, go slow; greater susceptibility to hypotension, conduction effects, and cinchonism. [1–3]
- Parenteral administration:
- Historically available IV (gluconate salt), but hypotension and proarrhythmia limit parenteral cardiac use. Oral regimens predominate when quinidine is selected. [1,2]
Practical dosing pearls:
- Target the lowest effective dose that maintains rhythm control without widening QRS >25% or prolonging QTc dangerously.
- Space dose changes by at least one to two half-lives, with interim ECG checks. [1–3]
Contraindications and Precautions
- Absolute/major:
- Known hypersensitivity to quinidine or other cinchona alkaloids. [1–3]
- Previous quinidine-induced thrombocytopenia or hemolytic reactions. [1]
- Significant AV block or intraventricular conduction defects without a pacemaker. [1–3]
- Prolonged baseline QT, history of torsades de pointes, congenital long QT syndrome. [1–3]
- Concomitant use of potent QT-prolonging agents when alternative combinations are not possible. [1–3]
- Relative/caution:
- Heart failure, hypotension risk (alpha-blockade, negative inotropy). [1,2]
- Atrial flutter without AV nodal blockade (risk of 1:1 atrial flutter conduction). [2]
- Electrolyte disturbances (hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia), bradycardia. [1–3]
- Myasthenia gravis (antimuscarinic effects may worsen). [2]
- Severe hepatic dysfunction; significant renal impairment. [1–3]
Adverse Effects
Common, dose-related, and idiosyncratic reactions are characteristic; vigilance is essential.
- Cardiovascular:
- Torsades de pointes (potentially fatal polymorphic VT) due to QT prolongation. Risk increases with hypokalemia/magnesemia, bradycardia, high serum levels, concomitant QT-prolonging drugs, female sex, and structural heart disease. [1–3]
- Worsening heart block or excessive QRS widening; negative inotropy may exacerbate heart failure. [1–3]
- Hypotension (more prominent with rapid IV administration). [1,2]
- CNS and sensory (cinchonism):
- Tinnitus, hearing loss, headache, dizziness, blurred vision, sometimes nausea and vomiting. Early signs warrant dose reduction; severe cases prompt discontinuation. [1–3]
- Gastrointestinal:
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain; relatively common and sometimes dose-limiting. [1–3]
- Hematologic and immune:
- Immune thrombocytopenia (can be severe), hemolytic anemia; fever and rash may accompany hypersensitivity. Periodic CBC recommended in prolonged therapy. [1,2]
- Hepatic:
- Hepatitis and cholestatic injury (idiosyncratic). Monitor LFTs if symptoms (jaundice, dark urine, pruritus) occur. [1,2]
- Dermatologic:
- Rash, photosensitivity, rare severe cutaneous reactions. [1,2]
Clinical tip: “Quinidine syncope” in historical descriptions often reflected torsades-mediated transient loss of consciousness; always interrogate QTc and precipitating factors. [1–3]
Major Drug–Drug Interactions
- Transporter-mediated:
- P-gp inhibition: Raises concentrations of digoxin and other P-gp substrates.
- Digoxin: anticipate ~doubling of levels; reduce digoxin dose (often by ~50%) and monitor closely. [1,2]
- P-gp inhibition: Raises concentrations of digoxin and other P-gp substrates.
- Cytochrome P450:
- Strong CYP2D6 inhibitor: Elevates exposure to 2D6 substrates (e.g., metoprolol, carvedilol, many TCAs, certain SSRIs/SNRIs, antipsychotics, codeine/tramadol activation impaired, flecainide, propafenone). Dose adjust substrates and monitor for toxicity or reduced prodrug activation. [1,2]
- CYP3A4 substrate:
- Inhibitors (e.g., azoles, macrolides, certain protease inhibitors, grapefruit) may increase quinidine levels and torsades risk.
- Inducers (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St John’s wort) may reduce efficacy. [1,2]
- Additive QT prolongation:
- Avoid with other QT-prolonging antiarrhythmics (e.g., dofetilide, sotalol, amiodarone), macrolides, fluoroquinolones, certain antipsychotics, and methadone when possible. [1–3]
- Additive AV nodal/cardiac effects:
- With beta-blockers/non-DHP CCBs: desired for AF rate control but increases risk of bradycardia/AV block—dose carefully and monitor. [2]
- Anticoagulants:
- Potential for altered warfarin effects via protein binding and metabolic interactions; monitor INR. [1,2]
Always reassess the full medication list (including OTC/herbal products) before initiating quinidine. [1–3]
Monitoring
- Before initiation:
- Baseline ECG (PR, QRS, QTc), serum electrolytes (K+, Mg2+, Ca2+), renal and hepatic function. Review drug interactions. [1–3]
- During therapy:
- ECG after dose changes; watch for QRS >25% increase or QTc >500 ms or >60 ms increase.
- Serum quinidine concentrations (e.g., trough 2–6 µg/mL) when available.
- Electrolytes maintained at high-normal; supplement K+/Mg2+ as needed.
- CBC and LFTs periodically with chronic use. [1–3]
- Symptoms surveillance:
- Dizziness, syncope, palpitations (possible torsades); tinnitus or visual changes (cinchonism); GI intolerance; bleeding/bruising (thrombocytopenia). [1–3]
Special Populations
- Elderly:
- Increased sensitivity to hypotension, conduction effects, and CNS toxicity. Start low, titrate cautiously, monitor closely. [1–3]
- Hepatic impairment:
- Reduced clearance; lower doses and more frequent monitoring. [1,2]
- Renal impairment:
- Some renal excretion; consider dose reduction in severe impairment and monitor levels. [1,2]
- Heart failure:
- Negative inotropy and proarrhythmic risk warrant caution; alternatives often preferred. [1–3]
- Pregnancy:
- Historical use for malaria suggests potential use when benefits outweigh risks; crosses placenta; fetal monitoring recommended if used for arrhythmias. Consult specialist and current guidance. [1,2]
- Lactation:
- Excreted into breast milk in small quantities; observe infant for irritability or feeding issues if maternal use is unavoidable. [1,2]
- Pediatrics:
- Limited, specialist-guided use with careful dosing and monitoring. [1,2]
Toxicity and Overdose
- Clinical features:
- Marked QT prolongation and torsades de pointes, widened QRS, high-grade AV block, ventricular arrhythmias, severe hypotension, CNS disturbances (confusion, seizures), and severe GI distress. [1–3]
- Management:
- Airway/ventilation, continuous cardiac monitoring.
- For torsades: IV magnesium sulfate; correct K+/Mg2+; consider temporary overdrive pacing or isoproterenol if bradycardia-dependent. [1–3]
- For Na+ channel blockade with wide QRS and hemodynamic compromise: IV sodium bicarbonate boluses. [1–3]
- Vasopressors for refractory hypotension; avoid agents that further prolong QT.
- Activated charcoal if early; multi-dose charcoal may enhance elimination due to enterohepatic cycling. Hemodialysis is generally ineffective due to protein binding and large Vd. [1,2]
- Discontinue offending interacting drugs; consult a medical toxicologist/poison center. [1–3]
Comparative Profile: Quinidine vs Other Antiarrhythmics
- Within Class IA:
- Procainamide: Similar Na+ and K+ effects; less antimuscarinic action; active metabolite N-acetylprocainamide (NAPA) prolongs repolarization; parenteral use more common acutely; lupus-like syndrome risk with chronic use. [1,2]
- Disopyramide: Stronger negative inotropy and antimuscarinic effects; can exacerbate heart failure; sometimes chosen for vagally mediated AF due to anticholinergic properties. [1,2]
- Vs Class IC (flecainide, propafenone):
- IC agents cause marked Na+ block without APD prolongation; effective in AF in structurally normal hearts but contraindicated post-MI/structural disease. Quinidine’s K+ block increases torsades risk; both classes carry proarrhythmia in susceptible patients. [2]
- Vs Class III (amiodarone, sotalol, dofetilide):
- Class III drugs primarily prolong repolarization; amiodarone has lower torsades risk but myriad extracardiac toxicities; sotalol/dofetilide demand QT and renal-function monitoring. Quinidine combines conduction slowing with APD prolongation and antimuscarinic effects, which can be disadvantageous in AF without rate control. [1–3]
Clinical role today: Quinidine is seldom first-line; it is considered when a specific electrophysiologic profile is desired (e.g., some inherited syndromes) or when other therapies are ineffective or contraindicated. [1–3]
Practical Prescribing Approach
- Candidate selection: Confirm indication where quinidine adds value and alternatives are limited or unsuitable. [1–3]
- Pre-treatment:
- Baseline ECG and labs; correct electrolytes.
- Review and modify interacting medications (especially digoxin, 2D6 substrates, QT-prolonging agents).
- Establish a plan for rate control if AF/flutter is targeted. [2]
- Initiation and titration:
- Start with a low dose; recheck ECG after 2–3 doses and after any change.
- Consider inpatient initiation for higher-risk patients (structural heart disease, baseline prolonged QT, concomitant QT-prolonging drugs). [1–3]
- Monitoring:
- ECGs at steady state and when clinically indicated.
- Drug levels when available, especially if efficacy/toxicity is unclear.
- Regular electrolyte checks; maintain K+ >4.0 mmol/L and Mg2+ >2.0 mg/dL when feasible. [1–3]
- When to stop:
- QTc >500 ms or >60 ms increase from baseline with no reversible contributors; torsades or sustained ventricular arrhythmia; immune thrombocytopenia; severe cinchonism or intolerable GI effects. [1–3]
Case-based Pearls
- A 68-year-old with paroxysmal AF and mild LVH: Quinidine would not be preferred; consider alternatives (e.g., dofetilide, amiodarone) with careful QT monitoring. If quinidine is chosen, preload with a beta-blocker, monitor QTc closely, and use TDM. [1–3]
- A 35-year-old with Brugada syndrome and recurrent ICD shocks: In expert centers, quinidine may be employed to reduce ventricular arrhythmia burden by Ito/IKr block; ECG and QT surveillance is critical, and electrolyte optimization is mandatory. [1,3]
- A 75-year-old on digoxin and metoprolol: Quinidine would markedly increase digoxin levels and metoprolol exposure (2D6 inhibition), necessitating digoxin dose halving and metoprolol dose reduction with close monitoring—or preferably choosing a different antiarrhythmic to avoid interactions. [1,2]
Key Takeaways
- Class IA profile: Moderate Na+ block plus IKr block yields QRS widening and QT prolongation; antimuscarinic effects may speed AV nodal conduction. [1–3]
- Narrow therapeutic index: Requires ECG surveillance, electrolyte optimization, and often TDM; proarrhythmia (torsades) is the most feared complication. [1–3]
- High interaction burden: Strong inhibitor of CYP2D6 and P-gp; major interactions with digoxin and many cardio- and psychoactive drugs. [1,2]
- Modern role: Limited and specialized; prioritize safer alternatives when available. Select niche uses exist in inherited arrhythmia syndromes under expert care. [1–3]
References (Vancouver style)
- Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollmann BC, editors. Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 14th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2022.
- Katzung BG, Kruidering-Hall M, Trevor AJ. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. 15th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2021.
- Rang HP, Ritter JM, Flower RJ, Henderson G. Rang & Dale’s Pharmacology. 9th ed. London: Elsevier; 2019.
- Neal MJ. Medical Pharmacology at a Glance. 9th ed. Chichester, West Sussex: Wiley-Blackwell; 2015.
- Waller DG, Sampson AP. Medical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 5th ed. Edinburgh: Elsevier; 2018.
- Brody TM, Larner J, Minneman KP, Neu HC. Human Pharmacology: Molecular to Clinical. 5th ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 2010.
- Page CP, Curtis MJ, Sutter MC, Walker MJA, Hoffman BB. Integrated Pharmacology. 2nd ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 2002.
- Roden DM. Antiarrhythmic drugs. In: Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollmann BC, editors. Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 14th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2022.
- Trevor AJ, Katzung BG, Kruidering-Hall M. Pharmacology Examination & Board Review. 12th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2019.
- Howland RH. Drug therapy for cardiac arrhythmias. In: Brody’s Human Pharmacology: Mechanism-based Therapeutics. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2018.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.