Introduction: The Gatekeepers of Drug Development
Preclinical trials are the cornerstone of medical research and development. They serve as the critical “gatekeeper” stage in the long journey of bringing a new drug to market. While often simplified as “animal testing,” preclinical development is a highly regulated, scientifically rigorous process designed to bridge the gap between a chemical discovery and a human patient.
In regulatory terms (such as those of the FDA), the ultimate goal of preclinical trials is to gather enough safety data to file an Investigational New Drug (IND) application. Without a successful IND, a drug cannot legally enter Clinical Trials (Phase I-III).
Crucially, these studies must be conducted under Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) regulations. GLP is a strict quality system concerned with the organizational process and conditions under which studies are planned, performed, monitored, and reported. Data generated without GLP compliance is generally rejected by regulatory authorities.
What Are Preclinical Trials?
Preclinical trials are scientific studies conducted on non-human subjects—specifically in vitro (test tubes/cells) and in vivo (animals)—to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a new molecular entity (NME).
Unlike clinical trials, which focus on “does it work in people?”, preclinical trials focus on two key questions:
- Is it safe enough to give to humans? (Safety Pharmacology & Toxicology)
- Does it have a plausible mechanism of action? (Pharmacodynamics)
Phase 1: In Vitro Studies (The “Test Tube” Phase)
Before a drug ever enters a living system, it undergoes rigorous screening in the lab.
High-Throughput Screening (HTS)
Modern pharmacology utilizes High-Throughput Screening, where automated robots test thousands of chemical compounds against specific biological targets (like a receptor or enzyme) to identify “hits.”
Key In Vitro Assays
- Cell Culture Studies: Using specific cell lines (e.g., CHO or HEK cells) to see if the drug binds to the intended target.
- Permeability Studies (Caco-2): Determining if the drug can cross the gut wall (oral bioavailability) or the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB).
- Genotoxicity Screening (Ames Test): A critical early test using bacteria (Salmonella typhimurium) to check if the compound causes DNA mutations, which could lead to cancer.
- Metabolic Stability: Using liver microsomes to see how quickly the liver enzymes (Cytochrome P450) break down the drug.
Phase 2: Safety Pharmacology (The “Vital Systems”)
Reference: ICH S7A Guidelines
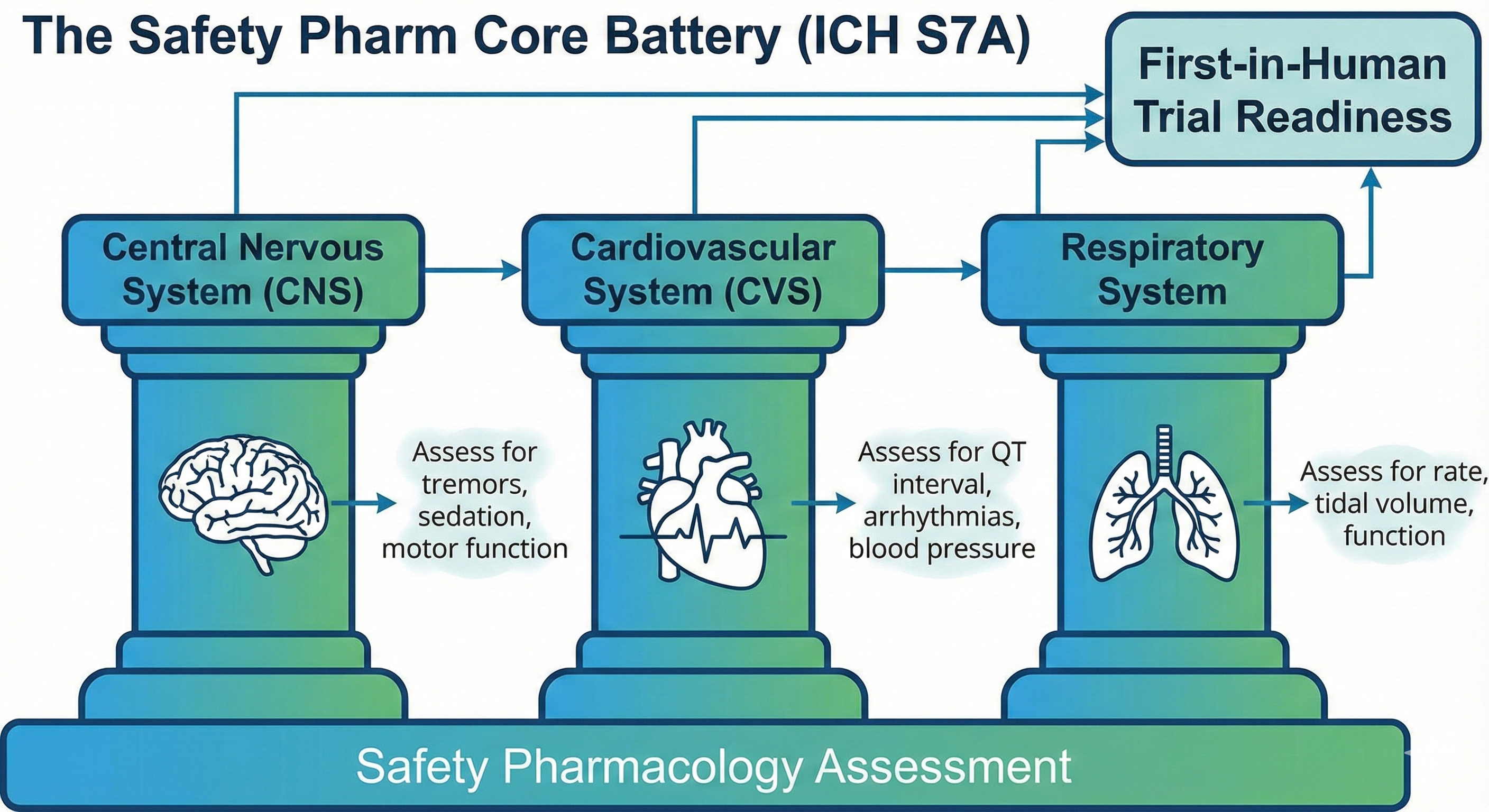
This is a distinct and critical step often confused with general toxicology. According to the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines, Safety Pharmacology specifically assesses whether a drug impairs the vital functions of the body at therapeutic doses.
Regulatory bodies require a “Core Battery” of tests to be completed before the first human dose:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Assessed (usually in rodents) using the Irwin Test or Functional Observation Battery (FOB). Researchers look for tremors, sedation, convulsions, or changes in motor activity.
- Cardiovascular System (CVS): The most critical safety check. Drugs are screened for QT interval prolongation (using the hERG assay in vitro and telemetry in dogs/monkeys). A prolonged QT interval can cause Torsades de Pointes, a potentially fatal heart arrhythmia.
- Respiratory System: Measuring tidal volume and respiratory rate to ensure the drug doesn’t suppress breathing.
Phase 3: Toxicology Studies (Defining the Limits)
While Safety Pharmacology looks at “vital signs” at therapeutic doses, Toxicology pushes the dose higher to find out what damage the drug causes when taken in excess.
Types of Toxicology Studies
- Acute Toxicity: Assesses the effects of a single, high dose. This helps identify the target organs of toxicity (e.g., does it damage the liver or the kidneys?).
- Sub-Acute / Sub-Chronic Toxicity: Repeated dosing (usually 2 weeks to 3 months) to simulate the duration of early human trials.
- Chronic Toxicity: Long-term exposure (6 months to 2 years) required for drugs intended for chronic human use (like blood pressure medication).
- Reproductive Toxicity: (Segment I, II, III studies) Assessing fertility, teratogenicity (birth defects), and development. This is mandatory to prevent tragedies like Thalidomide.
Calculating the Human Dose: The NOAEL
One of the most important outputs of preclinical trials is the NOAEL (No Observed Adverse Effect Level).
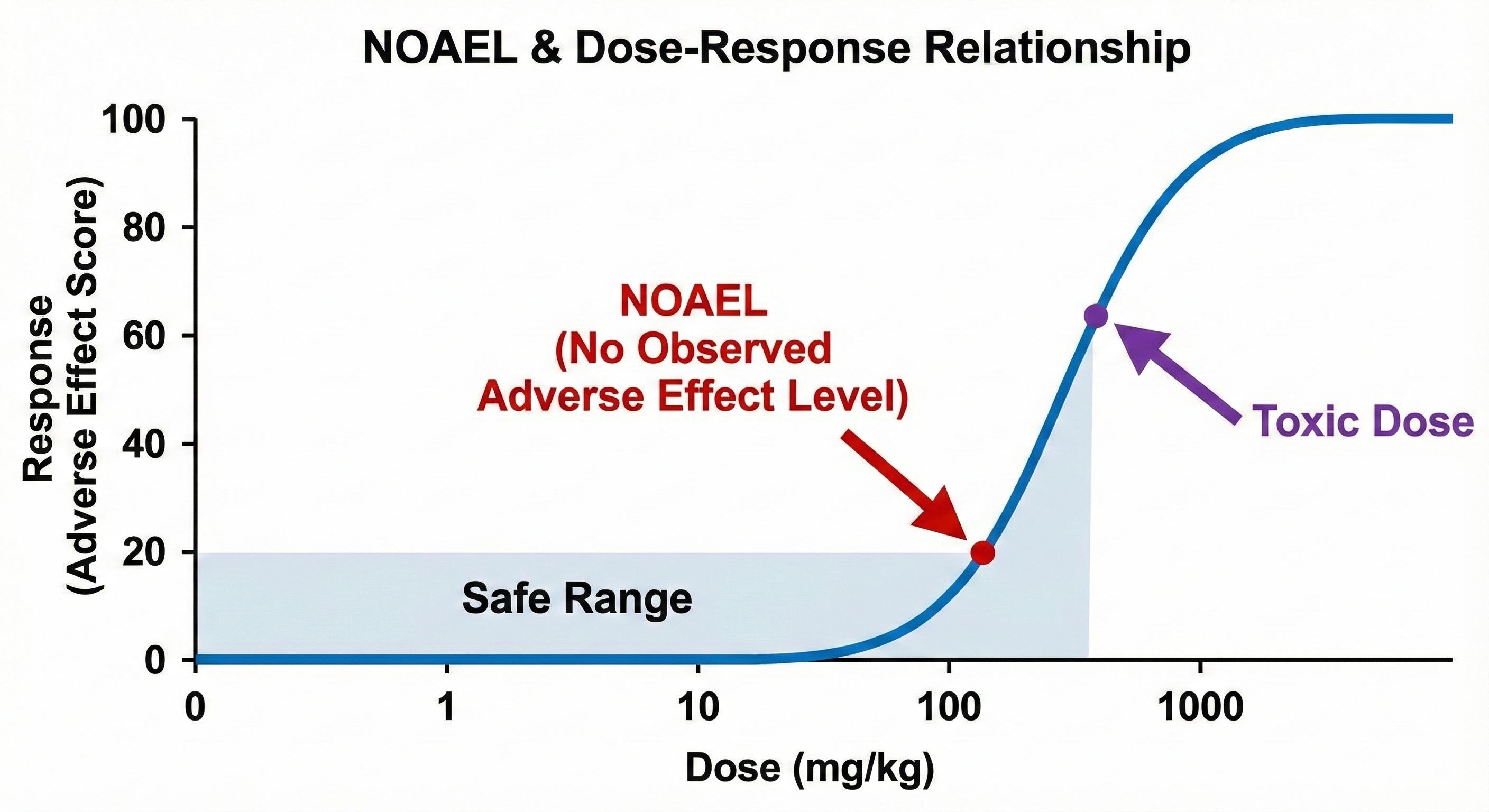
The NOAEL is the highest dose tested in animals that produces no significant adverse effects. Pharmacologists use the NOAEL to calculate the Maximum Recommended Starting Dose (MRSD) for humans. typically, the human starting dose is set at a safety factor (often 1/10th) of the NOAEL to ensure the first human volunteers are safe.
Animal Models in Research
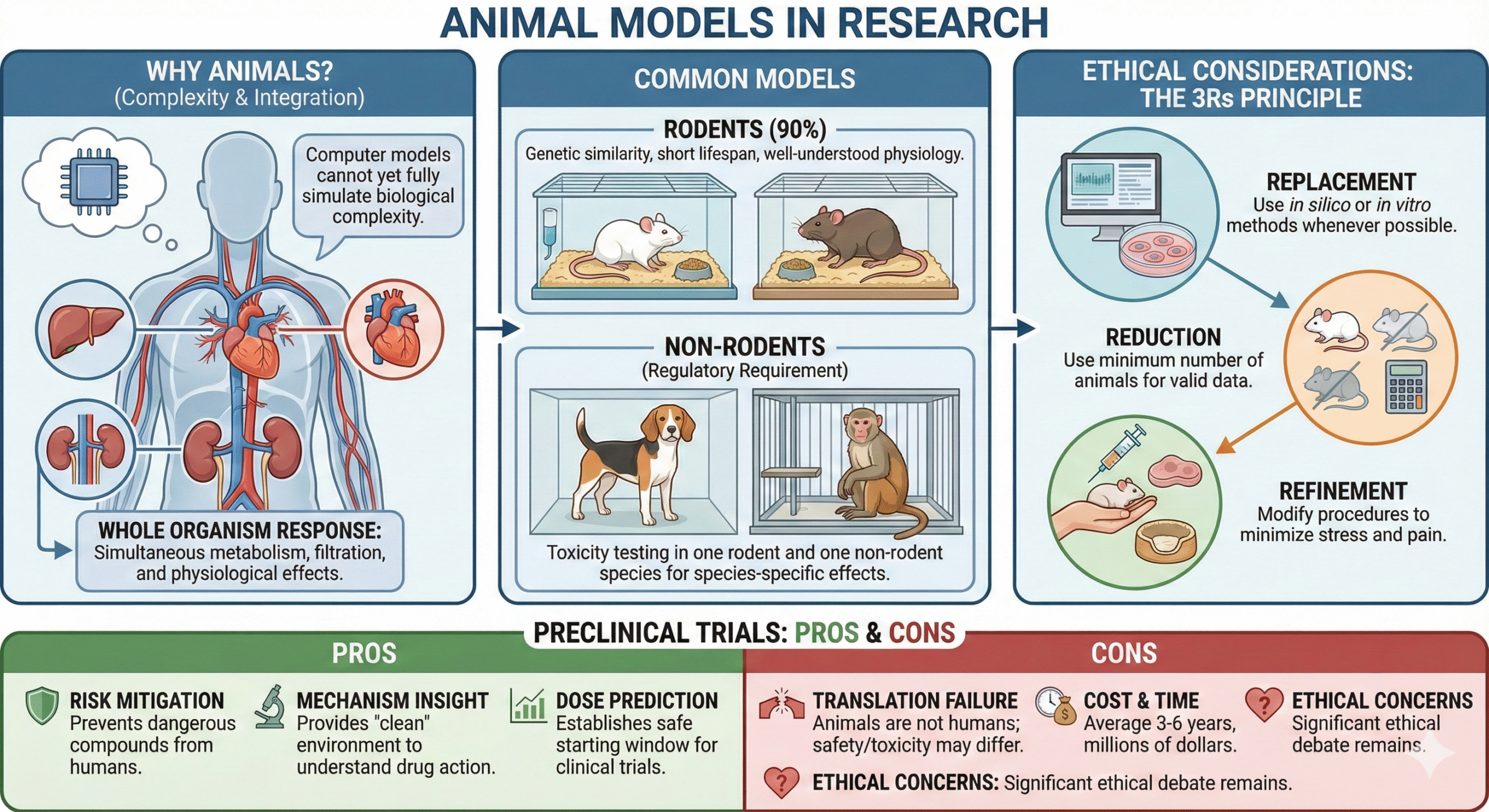
Why Animals?
Despite technological advances, computer models cannot yet fully simulate the complexity of a whole living organism—such as how a drug affects blood pressure while simultaneously being metabolized by the liver and filtered by the kidneys.
Common Models
- Rodents (Mice/Rats): Used for 90% of studies due to genetic similarity, short lifespan, and well-understood physiology.
- Non-Rodents (Dogs/Primates): Regulatory guidelines generally require toxicity testing in one rodent and one non-rodent species to identify species-specific effects.
Ethical Considerations: The 3Rs
Modern pharmacology is bound by strict ethical standards. Researchers must adhere to the 3Rs principle:
- Replacement: Using computer simulations (in silico) or cell cultures (in vitro) instead of animals whenever possible.
- Reduction: Using the absolute minimum number of animals necessary to get statistically valid data.
- Refinement: Modifying procedures to minimize stress and pain (e.g., better anesthesia, comfortable housing).
The Pros and Cons of Preclinical Trials
Pros
- Risk Mitigation: Prevents dangerous compounds from reaching humans.
- Mechanism Insight: Provides a “clean” environment to understand exactly how a drug works.
- Dose Prediction: Establishes the safe starting window for clinical trials.
Cons
- Translation Failure: Animals are not humans. A drug might be safe in a rat but toxic to a human (and vice versa).
- Cost & Time: It takes average 3-6 years and millions of dollars to complete this phase.
- Ethical Concerns: The use of animals remains a significant ethical debate.
Conclusion
Preclinical trials are far more than just “testing on mice.” They are a sophisticated, highly regulated science that combines high-tech molecular biology with systemic physiology. By identifying the NOAEL and clearing the Core Battery of safety tests, preclinical researchers ensure that when a clinical trial begins, the risk to human participants is minimized as much as science allows.
FAQs
What is the main purpose of preclinical trials?
The main purpose is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a new medical treatment before it is tested on humans.
How long do preclinical trials usually last?
The duration can vary, but it usually takes several months to a few years.
Are preclinical trials mandatory?
Yes, they are a regulatory requirement before moving on to clinical trials involving humans.
What are the alternatives to animal testing in preclinical trials?
Alternatives include in vitro studies and computer simulations.
How are preclinical trials funded?
Pharmaceutical companies, government grants, or research institutions usually fund them.
Do preclinical trials guarantee the success of a new treatment?
No, they are an initial step in the research and development process.
Quiz on Preclinical Trials
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.

