Enzyme inducers: How they are important in the clinical pharmacology?
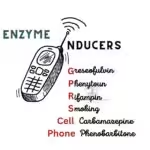
Introduction Enzyme inducers play a significant role in drug metabolism, affecting the efficacy and safety of various medications. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of enzyme inducers, explore their mechanisms of action, and provide relevant examples. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of enzyme inducers … Read more