Pharmacolgy of Atropine: antimuscarinic agent
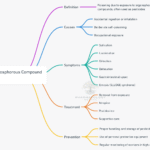
Introduction Atropine is a naturally occurring anticholinergic agent extracted from various plants of the Solanaceae family, most notably Atropa belladonna (deadly nightshade). Renowned for blocking muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, atropine exerts a range of physiological effects on the autonomic nervous system, thereby influencing everything from digestion and secretion to heart rate and ocular function. Because it … Read more