Macrolides are a group of antibiotics characterized by a macrocyclic lactone ring attached to various amino or neutral sugars. They are widely used in clinical medicine, particularly against respiratory pathogens and certain atypical organisms. Erythromycin was the first macrolide discovered (isolated from Streptomyces erythreus in the 1950s), followed by newer “second-generation” and “third-generation” agents such as clarithromycin, azithromycin, and roxithromycin. Recent newcomers (e.g., fidaxomicin) expand the therapeutic possibilities for specific infections like Clostridioides difficile.
Historically, macrolides served as an effective alternative to penicillin in penicillin-allergic patients. Today, macrolides remain integral in treating respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, sexually transmitted infections, and as part of combination regimens for Helicobacter pylori eradication and Mycobacterium avium complex prophylaxis. This overview addresses their structure, classification, mechanism of action, spectrum of activity, pharmacokinetics, clinical uses, adverse effects, resistance patterns, and emerging developments.
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
The Macrolide Ring
The hallmark feature of macrolides is the large (usually 14- to 16-membered) lactone ring. The classical agents (erythromycin, clarithromycin, roxithromycin) have a 14-membered ring, while azithromycin has a 15-membered lactone ring (often classified as an azalide). The variations in ring size and attached substituents influence their pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic properties.

Erythromycin structure
Commonly Used Macrolides
• Erythromycin: The prototype, usually formulated as salts or esters (e.g., stearate, ethylsuccinate) to improve GI stability.
• Clarithromycin: Semi-synthetic derivative of erythromycin with improved acid stability and oral bioavailability.
• Azithromycin: A 15-membered ring azalide with a long half-life and extensive tissue penetration.
• Roxithromycin: Similar to clarithromycin but less commonly used in some regions.
• Fidaxomicin: A newer, narrow-spectrum 18-membered ring macrolide mainly used for C. difficile infection management.
Macrolide Generations
While not always strictly categorized by “generations” as some antibiotic classes are, macrolides can be loosely grouped by their chronological development and structural properties:
• First-Generation: Erythromycin.
• Second-Generation: Clarithromycin, roxithromycin.
• Third-Generation: Azithromycin.
• Additional Agents: Telithromycin (a ketolide, structurally related but distinct), fidaxomicin, and others.
Mechanism of Action
Inhibition of Bacterial Protein Synthesis
Macrolides exert bacteriostatic (and sometimes bactericidal) effects primarily by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. Specifically, they bind near the peptidyl transferase center (PTC) of the 23S rRNA portion of the 50S subunit, blocking the exit tunnel and halting the translocation step of protein elongation.
Bacteriostatic vs. Bactericidal
Macrolides are generally considered bacteriostatic, but under certain conditions—high local concentrations, very susceptible strains, or specific organisms—they can exhibit bactericidal activity.
Additional Anti-inflammatory Effects
Macrolides, especially azithromycin, have been reported to modulate immune function and inhibit inflammatory cytokines. This property is partially responsible for their use in chronic inflammatory airway conditions (e.g., bronchiectasis).
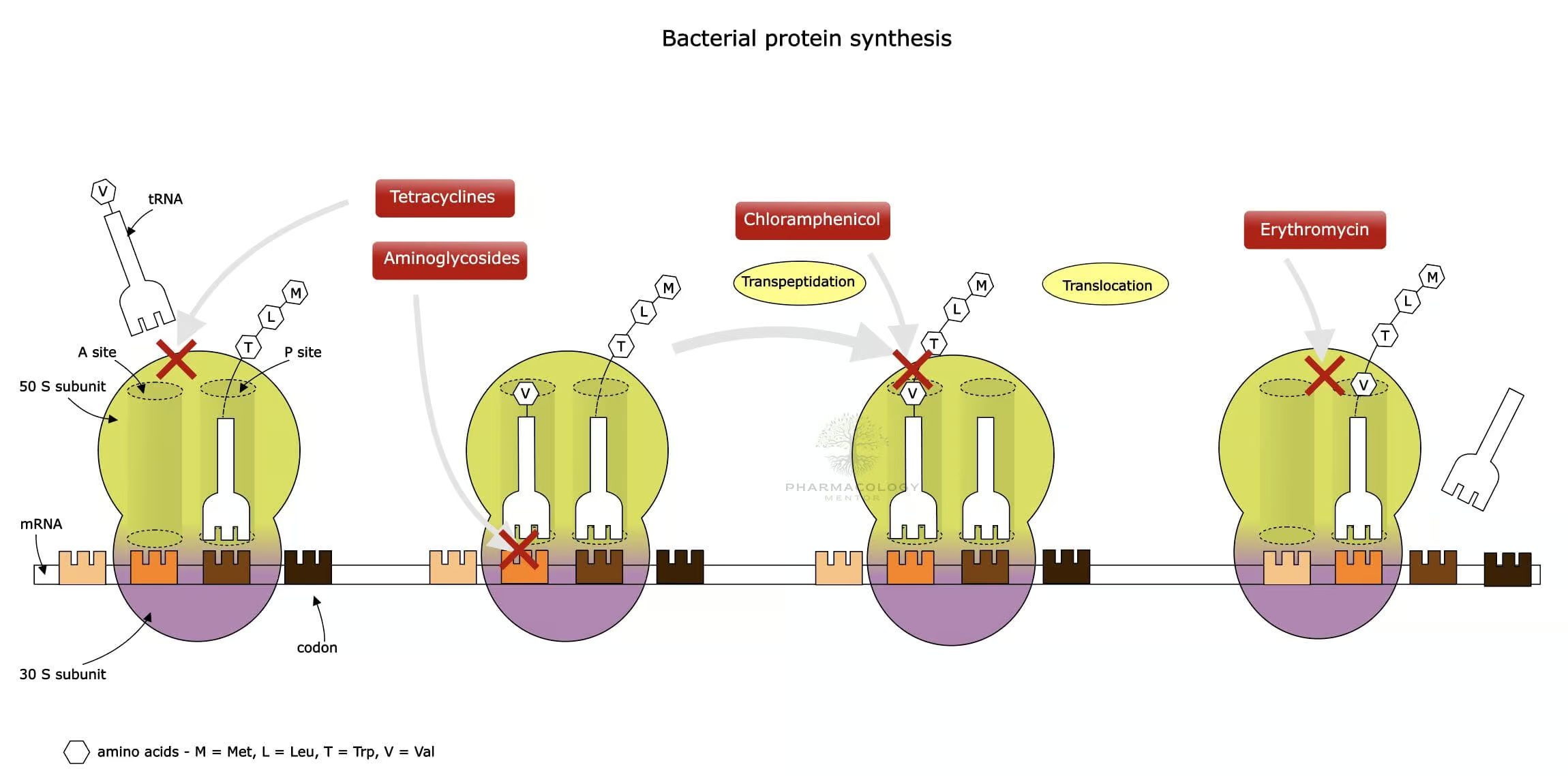
SPECTRUM OF ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY
Gram-Positive Organisms
Macrolides are often most effective against Gram-positive bacteria, including:
• Streptococcus pyogenes.
• Streptococcus pneumoniae (although resistance is growing).
• Staphylococcus aureus (mostly MSSA, though variable efficacy; not reliable for MRSA).
Atypical Pathogens
Macrolides are particularly recognized for efficacy against atypical respiratory pathogens:
• Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
• Chlamydophila pneumoniae.
• Legionella pneumophila.
Gram-Negative Organisms
Activity against Gram-negative rods is limited compared to fluoroquinolones or beta-lactams. However, macrolides cover:
• Haemophilus influenzae (better with clarithromycin & azithromycin than with erythromycin).
• Moraxella catarrhalis (generally susceptible).
• Bordetella pertussis.
• Campylobacter jejuni (azithromycin is a key choice).
Other Notable Bacteria
• Helicobacter pylori: Clarithromycin is a backbone of many H. pylori eradication regimens.
• Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC): Azithromycin and clarithromycin are pivotal for prophylaxis and treatment in immunocompromised individuals (especially HIV/AIDS with low CD4 counts).
• Treponema pallidum: Historically less effective than penicillin; not a primary macrolide target.
• Clostridioides difficile: Fidaxomicin is specifically indicated for C. difficile infections.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
• Erythromycin base is inactivated by gastric acid, so it often requires acid-resistant coatings or formulated as salts (e.g., stearate, ethylsuccinate).
• Clarithromycin and azithromycin demonstrate improved acid stability and bioavailability.
• Fidaxomicin is poorly absorbed from the GI tract, allowing high luminal concentrations for treating C. difficile in the colon.
Distribution
• Macrolides are generally well distributed in tissues, especially azithromycin, which achieves notably high intracellular concentrations, particularly in macrophages and lung tissue.
• Serum protein binding ranges from moderate to high, depending on the specific drug.
• CNS penetration is generally poor.
Metabolism
• Erythromycin and clarithromycin undergo hepatic metabolism (largely via CYP3A4), producing active and inactive metabolites.
• Azithromycin is less reliant on hepatic metabolism, giving it fewer CYP-mediated interactions.
• Fidaxomicin is minimally systemically absorbed; what little enters circulation is metabolized via hydrolysis.
Excretion
• Biliary excretion is predominant for most macrolides; a portion is renally excreted.
• Clarithromycin’s active metabolite is partially excreted by the kidneys, thus dosing adjustments may be considered in significant renal impairment.
Half-Life and Dosing
• Erythromycin: Requires multiple daily dosings (often QID or TID).
• Clarithromycin: Usually twice daily. Extended-release formulations allow once-daily dosing.
• Azithromycin: Notable for a long half-life (up to ~68 hours), enabling once-daily dosing for 3–5 days in many infections.
• Fidaxomicin: Typically given twice daily for 10 days for C. difficile infection.
Clinical Uses
Respiratory Tract Infections
• Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP): Macrolides (especially azithromycin) are front-line agents for covering atypical pathogens. Guidelines often recommend them alone (in mild outpatient CAP) or combined with beta-lactams for moderate/severe cases.
• Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis: Macrolides serve as an alternative to penicillin in streptococcal infections if patients are allergic to beta-lactams.
• Pertussis (Whooping Cough): Macrolides are the treatment of choice for Bordetella pertussis.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
• Mild to moderate infections caused by streptococci or susceptible staphylococci, especially in penicillin-allergic patients.
Sexually Transmitted Infections
• Chlamydia trachomatis: Azithromycin single-dose therapy is a mainstay for uncomplicated chlamydial infections.
• Gonorrhea (in combination): Historically, azithromycin was combined with cephalosporins, although guidelines now emphasize ceftriaxone monotherapy for gonorrhea due to resistance concerns.
Helicobacter pylori Eradication
• Clarithromycin is a key agent in multiple combination regimens (with a proton pump inhibitor and either amoxicillin or metronidazole). However, rising clarithromycin resistance lowers success rates in many regions.
Mycobacterial Infections
• Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC): Macrolides (clarithromycin or azithromycin) are essential in prophylaxis for immunosuppressed patients and in combination treatment regimens.
Fidaxomicin Use
• Specific indication for Clostridioides difficile infection. Shows efficacy comparable or superior to vancomycin with a lower recurrence rate, although cost can be a limiting factor.
Chronic Inflammatory Airway Diseases
• Low-dose macrolides (particularly azithromycin) for prophylaxis in cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, or severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to reduce exacerbation frequency.
ADVERSE EFFECTS AND TOXICITY
Gastrointestinal Disturbances
• Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea are the most common side effects, partly due to macrolides’ motilin agonist activity (particularly strong with erythromycin).
Hepatotoxicity
• Elevated liver enzymes, cholestatic hepatitis, and hepatic dysfunction can occur, particularly with prolonged or high-dose therapy (and more commonly with older macrolides).
QT Interval Prolongation
• Macrolides can prolong the QT interval, risking torsades de pointes. This risk is especially notable with erythromycin and clarithromycin; caution is advised in patients with predisposing factors (e.g., existing QT prolongation, electrolyte imbalances).
Ototoxicity
• High doses, especially intravenous erythromycin or clarithromycin, can cause transient hearing loss or tinnitus.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
• Rare but includes rashes, urticaria, and very rarely anaphylaxis. Some severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR) like Stevens-Johnson syndrome have been reported.
Drug Interactions
Cytochrome P450 Metabolism
• Erythromycin and clarithromycin (but not azithromycin) can inhibit CYP3A4, leading to elevated levels of other drugs metabolized by the same pathway (e.g., warfarin, statins, certain benzodiazepines).
• This interaction can increase risk of myopathy (with statins), bleeding (with warfarin), or sedation (with midazolam).
QT-Prolonging Agents
• Concurrent use of other QT-prolonging drugs (e.g., certain antiarrhythmics, fluoroquinolones, antipsychotics) can further increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias.
Digoxin
• Macrolides may increase digoxin levels by affecting gut flora that normally inactivate digoxin or by direct pharmacokinetic interactions.
Theophylline
• Erythromycin and clarithromycin can reduce the clearance of theophylline, potentially causing toxicity (nausea, vomiting, CNS symptoms).
RESISTANCE
Target Site Modification
• Methylation of the 23S rRNA binding site (erm genes) can prevent macrolide binding. This mechanism commonly confers cross-resistance with lincosamides and streptogramin B (the MLS_B resistance phenotype).
Efflux Pumps
• Some bacteria (e.g., Streptococcus pyogenes) can acquire mef genes encoding efflux pumps that expel macrolides, leading to reduced intracellular concentrations.
Drug-Inactivating Enzymes
• Enzymatic hydrolysis or phosphorylation of the macrolide structure can render the antibiotic inactive, though this mechanism is less commonly encountered than methylation or efflux.
Clinical Implications
• Rising macrolide resistance in staphylococci, streptococci, and H. pylori strains reduces therapy success in certain regions.
• Local or institutional susceptibility patterns greatly influence macrolide selection and combination therapy.
SPECIAL POPULATIONS & PRECAUTIONS
Pediatric Use
• Macrolides are commonly used for pediatric infections such as pertussis or atypical pneumonia. Azithromycin’s once-daily dosing improves compliance, while clarithromycin is frequently used for pediatric H. pylori regimens.
• Be mindful of gastrointestinal side effects and weight-based dosing.
Pregnancy and Lactation
• Erythromycin has a long history of use in pregnancy (classified generally as Category B in the U.S.).
• Azithromycin and clarithromycin also see use in pregnancy, typically if no better alternative is available.
• Fidaxomicin shows minimal systemic absorption, but data on its use in pregnancy is more limited.
Hepatic or Renal Impairment
• Erythromycin and azithromycin are predominantly eliminated via the biliary route, but clarithromycin dose may require adjustments in renal impairment.
• In severe hepatic dysfunction, macrolide dosing warrants close monitoring due to risk of accumulation or hepatic adverse events.
Geriatric Patients
• Macrolides are generally well tolerated. Close attention to possible drug interactions (especially polypharmacy) and QT interval considerations is important in older adults.
EMERGING MACROLIDES AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS
Novel Agents and Ketolides
• Telithromycin (a ketolide) was developed to combat macrolide-resistant organisms through a higher affinity for the 50S ribosome and partial evasion of methylation-based resistance. However, hepatotoxicity concerns limit its use.
Fidaxomicin and Related Molecules
• Fidaxomicin stands out for its potent activity against C. difficile and reduced disruption of normal gut flora compared to vancomycin. Ongoing research focuses on evolving spinoffs or similar compounds.
Anti-Inflammatory Exploitation
• Long-term, low-dose macrolide therapy is being studied further for anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory purposes in diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis, and severe asthma.
Overcoming Resistance
• Combination therapies and novel derivatization of existing macrolides continue in development to counteract macrolide-resistant pathogens. Research invests in new molecules with improved stability, lesser CYP interactions, and broader coverage.
CONCLUSION
Macrolides have proven invaluable in the treatment of respiratory infections, atypical pneumonia, sexually transmitted infections, H. pylori eradication, and prophylaxis or therapy of specific mycobacterial diseases. Over the decades, structural modifications to the lactone ring have led to enhanced acid stability, better pharmacokinetics, fewer gastrointestinal effects, and broader or more potent activity.
Despite these improvements, macrolide resistance has become increasingly prevalent, compelling clinicians to rely on susceptibility testing and combination therapy. Additionally, the known side effects—particularly QT prolongation and CYP3A4 interactions—must be cautiously managed. The emergence of fidaxomicin, with its niche in C. difficile infection, emphasizes the diversity and adaptability of macrolide chemistry.
As antibiotic resistance escalates, macrolides continue to evolve through new derivatives (e.g., ketolides) and creative delivery methods. Clinicians must remain vigilant to optimize macrolide regimens, balance efficacy with potential toxicities or drug interactions, and uphold stewardship principles for preserving these vital antibiotics.
References / Suggested Readings:
• Mandell LA, et al. “Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Community-Acquired Pneumonia.” Clin Infect Dis.
• Blondeau JM. “Clarithromycin and Other Macrolides.” Infect Dis Clin North Am.
• LeBlanc L, et al. “Macrolides and gycosides – Mechanisms, Resistances, and Pharmacology.” Antimicrob Agents.
• US Food & Drug Administration. Labeling and Safety for Macrolides.
• UpToDate online medical resource for updated guidelines on macrolides and their clinical uses.
Note: Always consult regional guidelines, local antibiograms, and individual patient factors before prescribing any antimicrobial therapy.









