An Overview of Essential Medicines
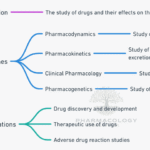
Essential medicines are drugs selected to meet the priority health care needs of a population, chosen on the basis of public‑health relevance, comparative efficacy and safety, cost‑effectiveness, and assured quality, forming the backbone of rational therapeutics, teaching, and formulary systems. Standard pharmacology textbooks present essential medicines as a framework that links evidence‑based drug selection with … Read more