The Comprehensive Guide to the Pharmacology of Androgens and Their Modulators
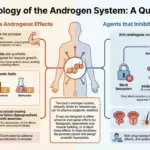
1. Introduction: Beyond the “Male Hormone” Androgens are a class of steroid hormones often simplified as “male hormones,” but their physiological reach extends far beyond that label, playing crucial roles in the development and health of both sexes. These substances are responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics and have profound effects on … Read more