Pharmacology of antiemetic drugs
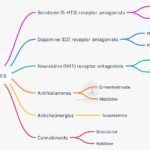
Introduction Nausea and vomiting are protective reflexes designed to prevent the ingestion or continued digestion of harmful toxins. However, when severe, they can significantly deteriorate patient comfort, compromise treatment adherence, and lead to complications such as electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, and undernutrition. Antiemetic drugs play a critical role across various clinical contexts—perioperative care, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, infectious gastroenteritis, … Read more