Routes of Drug Administration
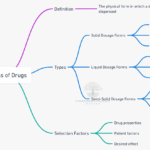
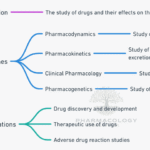
Introduction The administration of drugs is an essential aspect of medical practice. It involves the process of delivering medication to a patient’s body through various routes. The appropriate route of administration for a given situation depends on several factors, including the drug’s physical and chemical properties and patient-related factors. This chapter discusses the different routes … Read more