Introduction
Albendazole, a broad-spectrum anthelmintic, is effective against a range of intestinal and tissue helminth infections. It belongs to the benzimidazole class of compounds and is widely used in both human and veterinary medicine.
Chemical Structure and Properties
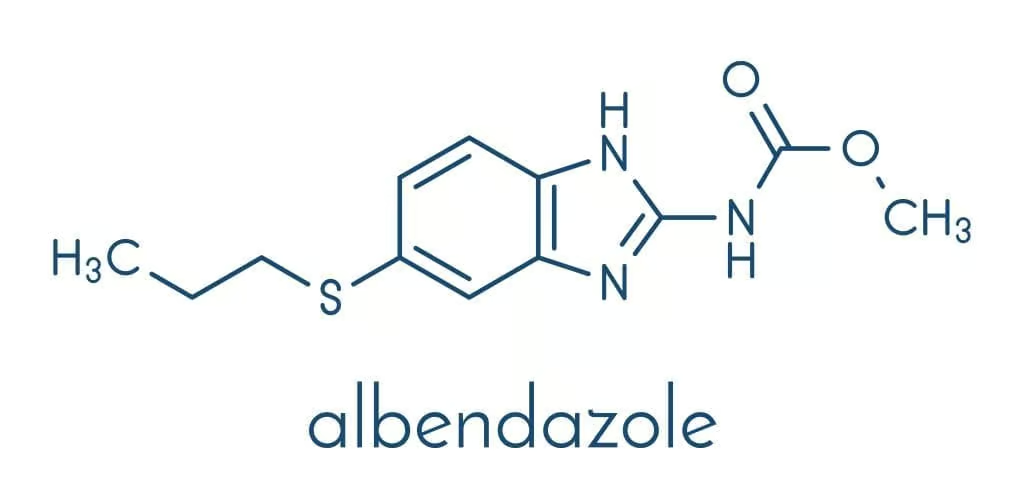
Albendazole is chemically described as methyl [5-(propylthio)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]carbamate. It is a white to off-white powder, poorly soluble in water and most organic solvents, but soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide.
Mechanism of Action
Albendazole works by inhibiting tubulin polymerization, which leads to the loss of cytoplasmic microtubules in intestinal and tegmental cells of the worm. This disruption of microtubule structures depletes the worm’s energy stores and leads to its death.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Its oral bioavailability is low due to its limited solubility. Absorption is significantly enhanced when administered with a fatty meal.
- Distribution: It is widely distributed throughout the body, including in the liver, bile, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, and tissues.
- Metabolism: Primarily metabolized in the liver to its active metabolite, albendazole sulfoxide, which possesses anthelmintic activity.
- Excretion: Excreted primarily in the bile and to a lesser extent in the urine.
Clinical Uses
- Intestinal Helminthiasis: Effective against a variety of intestinal worms, including Ascaris, hookworms, and whipworms.
- Tissue Helminthiasis: Used in the treatment of hydatid disease and neurocysticercosis, caused by the larval forms of the dog tapeworm and pork tapeworm, respectively.
- Other Uses: May have potential uses in the treatment of a range of protozoal infections and some cancers.
Adverse Effects
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- Hematological Effects: Neutropenia and, rarely, pancytopenia or agranulocytosis.
- Hepatic Dysfunction: Elevated liver enzymes and hepatotoxicity in prolonged use.
- Other Effects: dizziness, headache, fever, and hair loss.
Contraindications and Precautions
- Pregnancy: Contraindicated in pregnant women due to potential teratogenicity.
- Liver Disease: Caution in patients with hepatic impairment.
- Blood Disorders: Regular monitoring of blood counts in patients on prolonged therapy.
Drug Interactions
- CYP450 Enzymes: Co-administration with drugs that induce or inhibit CYP450 enzymes can affect albendazole metabolism.
- Antiepileptic Drugs: May reduce the efficacy of albendazole.
- Grapefruit Juice: Can increase plasma concentrations of albendazole sulfoxide.
Special Considerations
- Dosage in Children: Dosing adjustments may be necessary for pediatric patients.
- Administration with Food: To enhance absorption, albendazole should be taken with a fatty meal.
Conclusion
Albendazole is a key anthelmintic drug with broad-spectrum activity against a variety of parasitic worms. Its use, however, requires careful consideration of its pharmacokinetic properties, potential adverse effects, and interactions with other medications.









