Albendazole is a broad-spectrum benzimidazole anthelmintic that disrupts parasite microtubules and energy metabolism, leading to ovicidal, larvicidal, and vermicidal effects across key helminth infections. Clinically, it is FDA-approved for parenchymal neurocysticercosis and cystic hydatid disease, with established off-label utility against soil-transmitted helminths in accordance with public health guidance.
Overview
Albendazole is a synthetic methyl 5-(propylthio)-2-benzimidazolecarbamate used orally for tissue and intestinal helminthiases, recognized for wide distribution of its active metabolite to cyst fluid and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Although parent-drug plasma levels are negligible after oral dosing due to rapid first-pass conversion, clinical efficacy derives from albendazole sulfoxide, the principal active metabolite.
Chemical structure and Properties
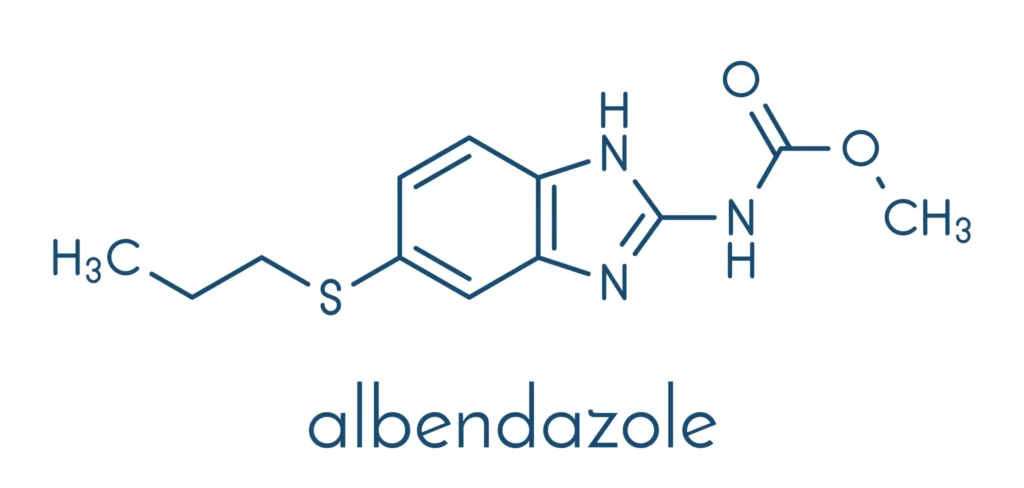
Albendazole is chemically described as methyl [5-(propylthio)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]carbamate. It is a white to off-white powder, poorly soluble in water and most organic solvents, but soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide.
Mechanism of action
Albendazole binds the colchicine-sensitive site on parasite β-tubulin, inhibiting polymerization and depleting functional microtubules essential for nutrient uptake and cell integrity. Resultant decreases in glucose transport and glycogen stores cause ATP depletion and death of larval and adult stages, explaining ovicidal and larvicidal activity in target organisms.
Antiparasitic spectrum
For labeled indications, albendazole is active against larval stages of Taenia solium (neurocysticercosis) and Echinococcus granulosus (cystic hydatid disease), aligning pharmacodynamic activity with tissue penetration of the sulfoxide metabolite. Beyond labels, authoritative summaries document efficacy across soil-transmitted helminths (ascariasis, trichuriasis, hookworm), strongyloidiasis, and selected protozoal contexts where local guidance supports its use.
Pharmacokinetics
Albendazole exhibits poor aqueous solubility and low oral absorption, but coadministration with a fatty meal increases albendazole-sulfoxide exposure up to fivefold, with peak concentrations at 2–5 hours and a typical half-life of 8–12 hours. The sulfoxide is 70% protein-bound and distributes into bile, liver, cyst wall, cyst fluid, and CSF at ratios lower than plasma, with biliary elimination predominating and urinary recovery of sulfoxide under 1% of dose.
Therapeutic indications
Regulatory approvals include parenchymal neurocysticercosis due to Taenia solium and cystic hydatid disease of the liver, lung, and peritoneum caused by Echinococcus granulosus. Evidence-based clinical practice also supports use in soil-transmitted helminth infections and other helminthiases where national or global public health guidance recommends albendazole-based regimens.
Dosing and administration
For neurocysticercosis and hydatid disease, adults ≥60 kg receive 400 mg twice daily with meals, while <60 kg receive 15 mg/kg/day in two divided doses (maximum 800 mg/day), with hydatid disease given in three 28-day cycles separated by 14-day drug-free intervals and neurocysticercosis typically for 8–30 days. For soil-transmitted helminths, CDC guidance recommends on-label schedules such as ascariasis 400 mg once, hookworm 400 mg once, and whipworm 400 mg daily for 3 days, generally on an empty stomach for intraluminal action, noting U.S. FDA labeling differences and local approvals.
Administration nuances
High-fat meals significantly enhance systemic albendazole-sulfoxide exposure and are preferred for tissue-invasive infections, whereas some public health guidance recommends fasting administration to prioritize intraluminal effects for intestinal luminal infections. Tablets may be chewed or crushed if needed, and oral suspension is available for patients with swallowing difficulties.
Adverse effects
Common adverse reactions include headaches, gastrointestinal upset, reversible alopecia, and elevated hepatic transaminases, with clinical trials noting LFT elevations in approximately 16% of hydatid disease patients. Serious hematologic events such as leukopenia, agranulocytosis, and pancytopenia are rare but reported; risk is higher in hepatic disease and echinococcosis, mandating periodic CBC monitoring during therapy.
Contraindications and warnings
Albendazole is contraindicated in those with hypersensitivity to benzimidazoles or product components, and carries boxed warnings for bone marrow suppression and embryo–fetal toxicity based on animal data and postmarketing experience. Before treating neurocysticercosis, evaluate for retinal cysticercosis to avoid sight-threatening inflammation from parasite death, and manage intracranial inflammation with appropriate corticosteroids and antiseizure prophylaxis.
Drug interactions
Coadministration with dexamethasone increases albendazole-sulfoxide troughs by about 56% and with praziquantel increases exposure by about 50% in the fed state, potentially augmenting central nervous system penetration and efficacy in neurocysticercosis. Cimetidine can increase biliary and cystic fluid sulfoxide concentrations approximately twofold, and cytochrome P450 induction or inhibition (for example, by enzyme inducers or inhibitors) may lower or raise systemic levels, respectively, with therapeutic and safety implications.
Special populations
In pregnancy, albendazole carries risk based on teratogenicity in animals, although limited human data have not shown clear increased risks; public health programs may allow use in the second and third trimesters when benefits outweigh risks in endemic settings. Albendazole and its sulfoxide appear in low concentrations in breast milk without reported infant harm, and pediatric pharmacokinetics after single doses are similar to adults when fed, supporting age-appropriate use under programmatic or clinical oversight.
Monitoring
Obtain baseline and q2-week CBC and hepatic transaminases during each 28-day treatment cycle and more frequently if abnormalities develop, with prompt discontinuation for significant cytopenias or hepatotoxicity. In suspected or epidemiologically at-risk patients, screen for neurocysticercosis before hydatid treatment to avoid unmasking neurologic disease, and perform ophthalmic evaluation prior to neurocysticercosis therapy to mitigate retinal injury.
Clinical pearls
- Use high-fat meals to maximize tissue exposure for neurocysticercosis and hydatid disease; consider fasting dosing for purely luminal infections following public health guidance and local approvals.
- Combine albendazole with corticosteroids and anticonvulsants for neurocysticercosis to reduce intracranial pressure–related complications and improve tolerability and outcomes.
- Adhere to cyclic therapy for hydatid disease and ensure surgical teams coordinate with medical therapy when perioperative sterilization of cysts or nonresectable disease control is required.
Resistance
Reduced binding affinity at β-tubulin due to amino acid substitutions is the principal mechanism of benzimidazole resistance, underscoring the importance of correct dosing, appropriate duration, and integration with surgical or interventional strategies when indicated. Surveillance of clinical response and adherence to evidence-based regimens help mitigate the emergence and impact of resistance in endemic programs.
Formulations and handling
Each film-coated tablet contains 200 mg of albendazole and can be chewed or crushed; store under controlled room temperature per manufacturer guidance to maintain stability and performance. Practical selection between tablets and suspension should reflect age, swallowing ability, and need for precise weight-based dosing in pediatric or low-body-weight patients.
References (Vancouver style)
- Albenza (albendazole) [package insert]. Impax Specialty Pharma; Revised 2019.
- Malik K, Dua A. Albendazole. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Apr 10.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical Care of Soil-transmitted Helminths. 2024 Nov 7.
- Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollmann BC, editors. Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 14th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2022.
- Katzung BG, Vanderah TW, editors. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. 16th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2021.
- Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, editors. Mandell, Bennett, & Dolin: Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2020.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.

