Pharmacotherapy of Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
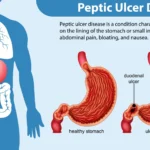
Introduction Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) encompasses the formation of ulcers in the stomach (gastric ulcer) or duodenum (duodenal ulcer), primarily caused by gastric acid hypersecretion and/or compromised defense of the gastric and duodenal mucosa. While Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection remains a principal etiology for many cases, other contributing factors include the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), stress-related mucosal injury, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (gastrinoma). Clinically, patients may present … Read more