Pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s Disease
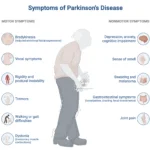
Introduction Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized predominantly by motor symptoms including bradykinesia, rest tremor, rigidity, and postural instability. These cardinal clinical features trace back to the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta, leading to reduced dopamine levels within the striatum of the basal ganglia. Along with the hallmark motor findings, patients often experience a variety of non-motor symptoms such as cognitive impairment, psychiatric manifestations, sleep disturbances, autonomic dysfunction, and sensory changes. … Read more