Steady-State Concentration: Principles, Calculations, and Clinical Application
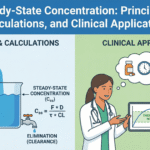
Steady state is a cornerstone concept in clinical pharmacokinetics. It connects dose, dosing interval, and patient-specific clearance to the drug concentrations that drive therapeutic and adverse effects. Yet, “steady state” is often misunderstood or oversimplified. This chapter explains what steady state is (and is not), how it arises under different dosing schemes, how to calculate … Read more