Antiarrhythmic drugs: Quinidine (Class 1A)
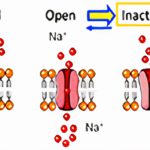
Overview and Learning Objectives By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Quinidine is a prototypical Class IA antiarrhythmic historically used in atrial and ventricular arrhythmias. Although its use has declined due to proarrhythmic risk and the emergence of better-tolerated alternatives, it remains an instructive archetype for understanding sodium channel–blocking drugs that … Read more