Antiarrhythmic drugs: Flecainide (Class 1C)
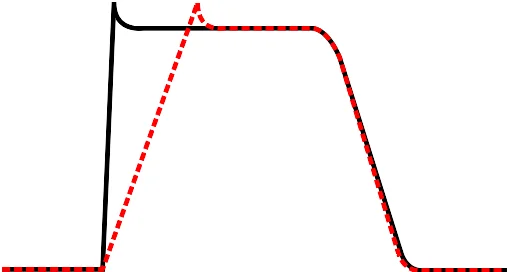
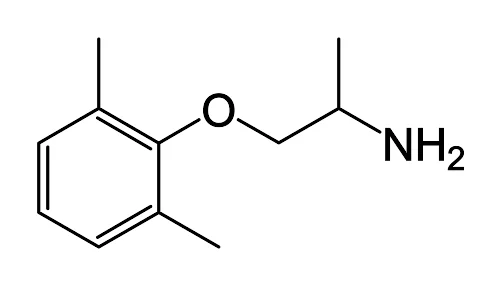
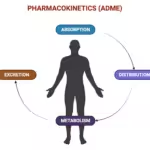
Flecainide is a Class 1C antiarrhythmic agent widely used for rhythm control in atrial and ventricular arrhythmias, particularly in patients without significant structural heart disease. The following summarizes its pharmacology, clinical uses, cautions, and monitoring, referencing key pharmacology textbooks and clinical reviews in Vancouver style. Overview Flecainide is a potent blocker of cardiac sodium (Na+) channels, … Read more