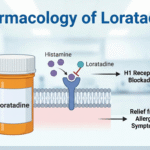
Pharmacology of Loratadine
Introduction Loratadine is a widely used second-generation antihistamine renowned for its effectiveness in alleviating allergy symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and itchy or watery eyes. By selectively blocking peripheral histamine H₁-receptors, loratadine significantly diminishes the effects of endogenous histamine, thus relieving the hallmark symptoms of allergic rhinitis, urticaria, and other hypersensitivity ailments. Thanks to its preferential targeting … Read more