Sodium Channel Blockers (SCBs)
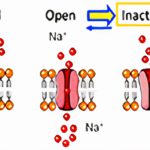
Introduction Sodium (Na⁺) channels are integral membrane proteins responsible for the rapid upstroke (phase 0) of the action potential in excitable cells such as neurons and cardiomyocytes. By selectively perming sodium ions across membranes, these channels facilitate depolarization, triggering electrical signals essential for neurotransmission, skeletal muscle contraction, and cardiac conduction. As a result, therapeutic modulation … Read more