Ischemic Heart Disease: Causes, signs and treatment options
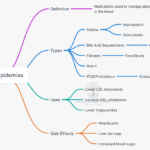
1. Definition & Epidemiology Ischemic heart disease (IHD)—also called coronary artery disease (CAD)—is defined by impaired blood supply (ischemia) to the myocardium, usually due to narrowing or obstruction of the coronary arteries by atherosclerotic plaque. IHD is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, particularly affecting adults over age 40 and those with major cardiovascular … Read more