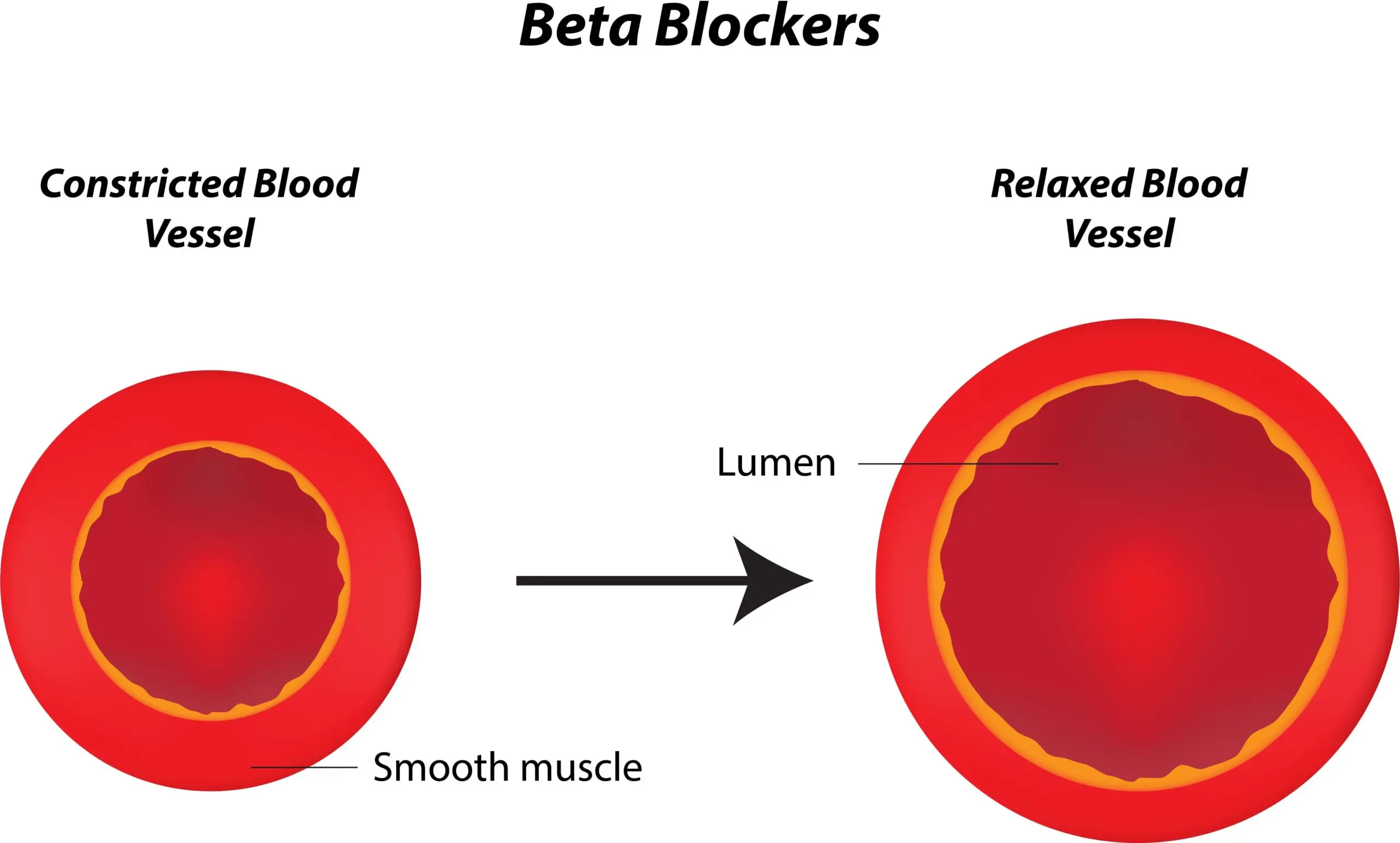
Introduction
Propranolol, a beta-adrenergic blocker, has been a mainstay in the treatment of various cardiovascular diseases. First synthesized in the 1960s, it revolutionized the management of conditions like hypertension, angina pectoris, and cardiac arrhythmias.
Chemical Structure and Properties
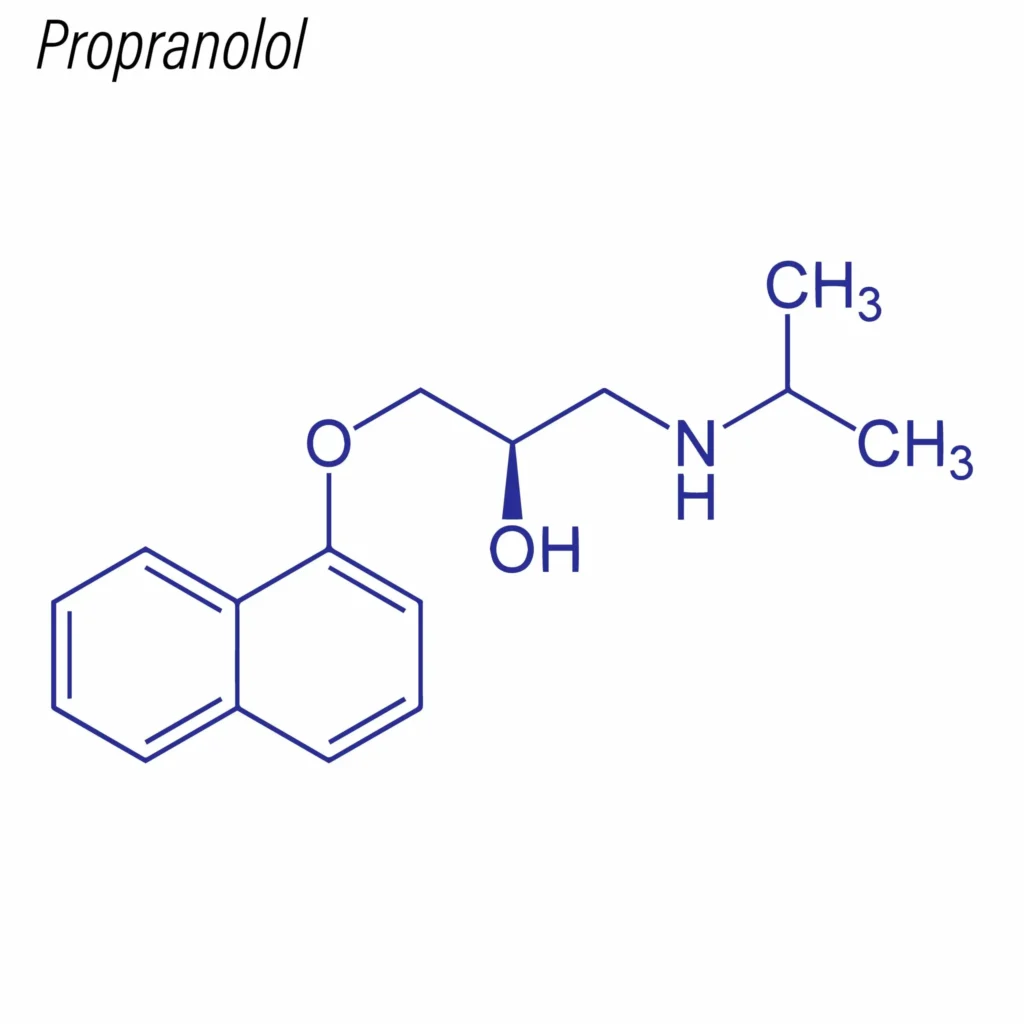
Propranolol is a synthetic, non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor antagonist. Its chemical structure is (RS)-1-(isopropylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)propan-2-ol. This lipophilic compound has a high degree of protein binding and a volume of distribution that indicates extensive tissue uptake.
Mechanism of Action
Propranolol’s primary mechanism is the blockade of beta-adrenergic receptors, particularly β1 and β2 receptors. This blockade results in:
- Decreased heart rate and myocardial contractility, reducing cardiac workload and oxygen demand.
- Inhibition of renin release from the kidneys, contributing to its antihypertensive effects.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Propranolol is almost completely absorbed after oral administration, but its bioavailability is reduced to about 25-35% due to extensive first-pass metabolism.
- Distribution: It is widely distributed throughout the body, crosses the blood-brain barrier, and is found in breast milk.
- Metabolism: Metabolized primarily in the liver through hydroxylation and conjugation.
- Excretion: Excreted predominantly in the urine, with a half-life of about 3 to 6 hours, which can be prolonged in patients with hepatic impairment.
Therapeutic Uses
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Including hypertension, angina pectoris, and certain types of tachyarrhythmias.
- Secondary Prevention of Myocardial Infarction: Reduces the risk of mortality and reinfarction.
- Other Uses: Effective in the prophylactic treatment of migraines, essential tremor, and in certain psychiatric conditions like performance anxiety.
Adverse Effects
- Cardiovascular: Bradycardia, hypotension, and in rare cases, heart failure.
- Respiratory: Bronchospasm, particularly in patients with a history of bronchial asthma.
- Central Nervous System: Fatigue, dizziness, and depression.
- Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort.
- Others: Hypoglycemia in diabetic patients, sexual dysfunction, and exacerbation of Raynaud’s phenomenon.
Contraindications and Precautions
- Contraindications: Asthma, COPD, severe bradycardia, second or third-degree heart block, and severe peripheral arterial disease.
- Precautions: Should be used with caution in patients with diabetes, thyroid disorders, and in those undergoing surgery.
Drug Interactions
Propranolol interacts with a variety of drugs. These include:
- Other Cardiovascular Drugs: Additive effects with other antihypertensives.
- CYP450 Modulators: Drugs that induce or inhibit hepatic enzymes can affect propranolol metabolism.
- Insulin and Antidiabetic Drugs: Altered hypoglycemic response.
- NSAIDs: Reduced antihypertensive effect.
- Anesthetic Agents: Increased risk of hypotension and bradycardia.
Special Considerations
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Propranolol crosses the placenta and is found in breast milk. Its use during pregnancy and lactation should be carefully considered.
- Elderly Patients: May require dose adjustments due to decreased hepatic function and increased sensitivity to the drug’s effects.
Future Perspectives
Emerging research indicates potential new therapeutic uses and formulations of propranolol, expanding its clinical applicability.
Conclusion
Propranolol, with its multifaceted pharmacological actions, remains a versatile drug in clinical medicine. Its comprehensive understanding is crucial for optimizing therapeutic outcomes while minimizing adverse effects.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.