Understanding “drug potency” and “drug efficacy” is crucial in pharmacology, as they describe a drug’s performance and are often used to compare different drugs. These terms are closely related to the dose-response curve (DRC).
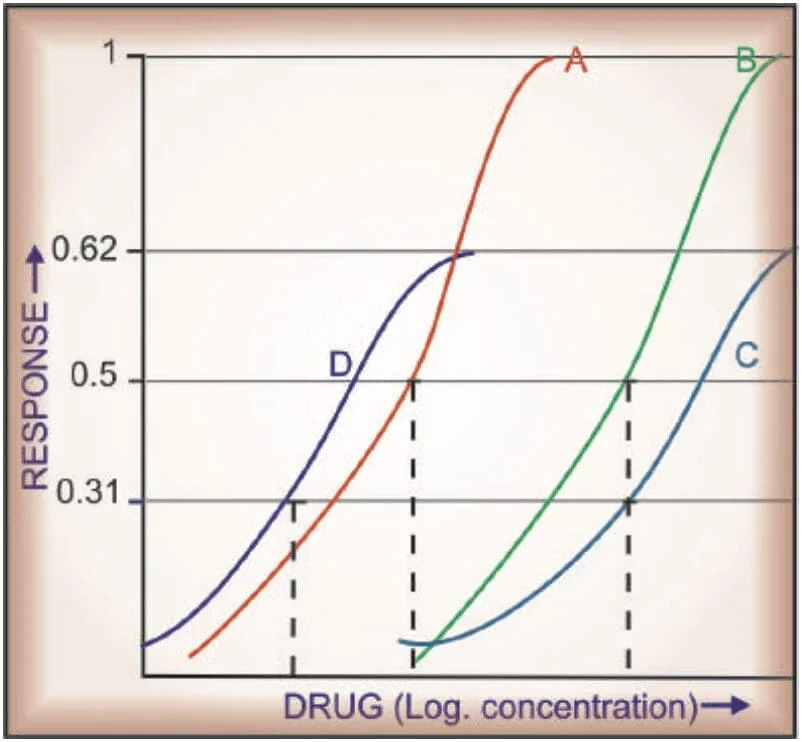
- Drug Potency: This term refers to the amount of a drug needed to produce a certain effect. A potent drug produces its desired effect at a low concentration. On the dose-response curve, potency is reflected by the position of the curve along the x-axis (dose); the further left the curve, the more potent the drug.
- Drug Efficacy: Efficacy is about the maximum effect a drug can produce, regardless of dose. It’s a measure of how effectively a drug achieves its desired effect in the body. On the dose-response curve, efficacy is indicated by the height of the curve along the y-axis (effect). A drug with higher efficacy will reach a higher plateau on the curve, indicating a greater maximal effect.
Dose-Response Curve (DRC) and Drug Potency
The DRC is a graphical representation that shows the relationship between the dose of a drug and the magnitude of its effect. The position of the DRC on the dose axis serves as an index of drug potency. Potency refers to the amount of drug needed to produce a specific response. A DRC that is positioned to the right on the dose axis indicates lower potency, while one that is positioned to the left indicates higher potency.
For example, if 10 mg of morphine produces the same analgesic effect as 100 mg of pethidine, morphine is considered 10 times more potent than pethidine. However, it’s important to note that higher potency does not necessarily mean clinical superiority. Potency is a factor in determining the dose of a drug but does not indicate the maximum effect a drug can produce.
Drug Efficacy
Efficacy refers to the maximal response that can be elicited by a drug. In other words, it describes the upper limit of a drug’s capability. For instance, morphine can produce a degree of analgesia that is not achievable with any dose of aspirin, making morphine more efficacious than aspirin.
Potency vs. Efficacy
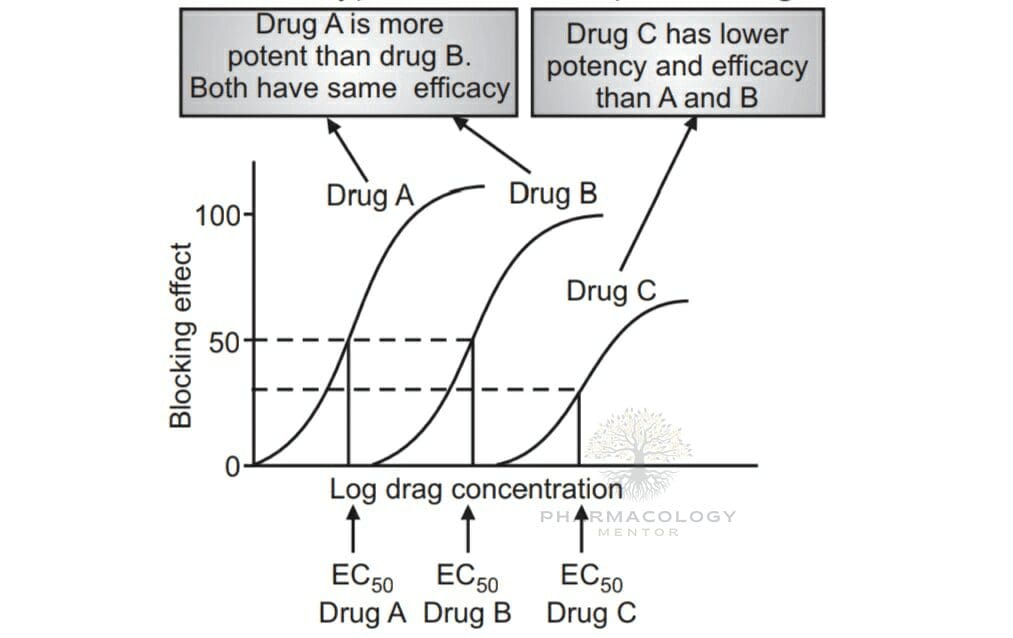
While these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they refer to different characteristics of a drug:
- Aspirin is less potent and less efficacious as an analgesic than Morphine.
- Pethidine is less potent but equally efficacious as an analgesic as Morphine.
- Furosemide is less potent but more efficacious as a diuretic than Metolazone.
- Diazepam is more potent but less efficacious as a CNS depressant than Pentobarbitone.
Clinical Implications
- Efficacy is often a more decisive factor in the choice of a drug. A drug with higher efficacy may be preferred for conditions requiring a strong response.
- Potency is important for determining the dosage. A more potent drug will require a smaller dose to achieve the same effect, which could be beneficial in reducing the risk of side effects.
- Therapeutic Window: Both potency and efficacy contribute to defining the therapeutic window, which is the range of doses that produces therapeutic effects without unacceptable side effects.
Conclusion
Understanding drug potency and efficacy is essential for making informed decisions in both drug development and clinical practice. These parameters, often derived from the DRC, provide valuable insights into the dose and the maximal effect of a drug, guiding healthcare professionals in optimizing treatment plans.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.