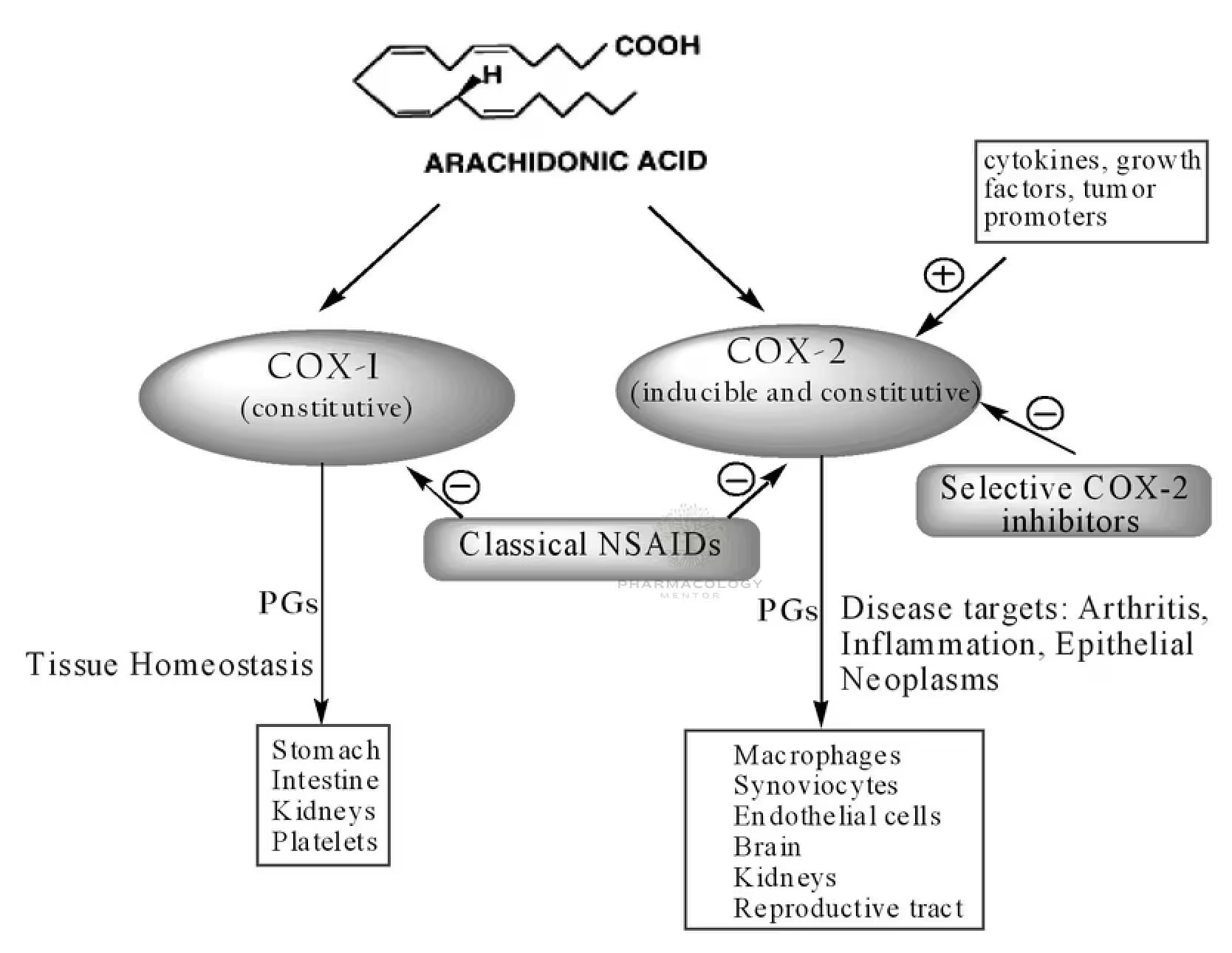
Cyclooxygenase (COX), which is also called prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase (PTGS), is an enzyme that converts arachidonic acid into prostanoids like thromboxane and prostaglandins like prostacyclin. This enzyme is a member of the animal-type heme peroxidase family and is also referred to as prostaglandin G/H synthase. The specific reaction it catalyzes involves the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2 through a short-lived prostaglandin G2 intermediate.
Pharmaceutical inhibition of COX can alleviate symptoms of inflammation and pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like aspirin and ibuprofen, work by inhibiting COX. Specific inhibitors of the COX-2 isozyme are termed COX-2 inhibitors. The active metabolite of paracetamol, AM404, is also a COX inhibitor, which is believed to contribute to its therapeutic effect.
In medical contexts, “COX” is more commonly used than “PTGS”. However, in genetics, “PTGS” is the official term for this family of genes and proteins, as “COX” was already designated for the cytochrome c oxidase family. Therefore, the two isozymes found in humans, PTGS1 and PTGS2, are often referred to as COX-1 and COX-2 in medical literature.
Thought-Provoking Questions/Insights:
- Pharmaceutical Implications: How might the understanding of COX enzymes influence the development of new anti-inflammatory drugs?
- Dietary Influence: Given that certain foods and supplements can influence COX activity, how might diet play a role in inflammation and pain management?
- Safety Concerns: With the withdrawal of certain COX-2 inhibitors due to cardiovascular concerns, how can the balance between therapeutic benefits and potential risks be achieved?
Cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes play a pivotal role in synthesizing prostaglandins, which are lipid compounds that mediate various physiological processes, including inflammation, pain, and fever. There are two main types of COX enzymes: COX-1 and COX-2.
Comparison Table: COX-1 vs. COX-2
| Feature | COX-1 (Constitutive) | COX-2 (Inducible) |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Found in most tissues | Produced at sites of inflammation |
| Function | Housekeeping functions; protects the stomach lining, supports kidney function, and promotes platelet aggregation. | Mediates inflammation, pain, and fever; supports kidney function. Promotes vasodilation |
| Expression | Constitutively expressed (always present) | Induced by inflammatory stimuli, cytokines, and growth factors |
| Inhibitors | Non-selective NSAIDs (e.g., aspirin, ibuprofen) | COX-2 selective inhibitors (e.g., celecoxib) |
| Role in Gastric Protection | Protects the gastric mucosa by producing prostaglandins that stimulate mucus and bicarbonate secretion | Not directly involved in gastric protection |
| Role in Kidney Function | Regulates renal blood flow and salt balance | Involved in salt and fluid balance under certain conditions |
| Role in Platelet Aggregation | Promotes platelet aggregation | Does not significantly affect platelets |
Key Points:
- COX-1 is constitutively expressed, meaning it’s always present in the cells. It involves many normal physiological processes, such as protecting the stomach lining and promoting platelet aggregation.
- COX-2, on the other hand, is usually not present in cells but is induced or upregulated during inflammatory responses. It’s primarily responsible for producing prostaglandins that mediate inflammation, pain, and fever.
Both enzymes are targets for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Traditional NSAIDs like aspirin and ibuprofen inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2, while some newer NSAIDs are designed to specifically inhibit COX-2, aiming to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects associated with COX-1 inhibition.
COX-3
COX-3, also known as prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 3 (PTGS3), is a splice variant of COX-1. It is thought to be involved in inflammation, but its role is still not fully understood. COX-3 is expressed in a variety of tissues, including the brain, spinal cord, and heart. It is also expressed in platelets, but at a lower level than COX-1.
COX-3 produces prostaglandins, which are involved in a variety of functions in the body, including pain, inflammation, and fever. However, the exact role of COX-3 in these functions is still not fully understood.
Some studies have shown that COX-3 inhibitors can relieve pain and inflammation. However, other studies have not found the same results. More research is needed to determine the exact role of COX-3 in pain and inflammation and to see if COX-3 inhibitors can be used to treat these conditions.
COX-3 inhibitors are a potential target for new drugs to treat pain and inflammation. However, more research is needed to determine the safety and efficacy of these drugs.
Medical Disclaimer
The medical information on this post is for general educational purposes only and is provided by Pharmacology Mentor. While we strive to keep content current and accurate, Pharmacology Mentor makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the post, the website, or any information, products, services, or related graphics for any purpose. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment; always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and never disregard or delay seeking professional advice because of something you have read here. Reliance on any information provided is solely at your own risk.